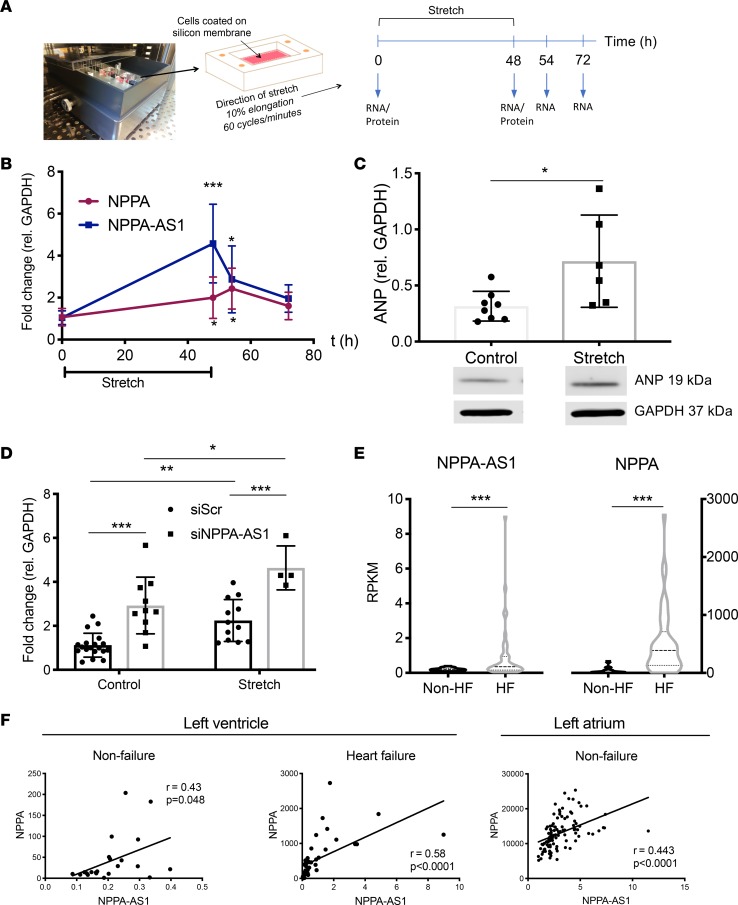
Figure 7. Mechanical strain increases NPPA and NPPA-AS1 expression in cardiomyocytes.
(A) Overview of the setup and design of the strain experiment. (B) NPPA and NPPA-AS1 expression during the time course of the experiment quantified by qRT-PCR. Expression is presented relative to GAPDH and normalized to the mean of the cells at time point 0 hours. Results are based on 3 separate experiments with 3 replicates in each group. Mean and standard deviation are shown. The Kruskal-Wallis test was used to test the difference in expression between baseline and each time point. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 after adjustment for multiple comparisons using Dunn’s test. (C) Protein levels of ANP at baseline and after 48 hours of stretch. Results are expressed relative to GAPDH protein levels. Data are from 2 separate experiments with 3–4 replicates in each group. Shown are mean and standard deviation in each group. *P < 0.05 by Mann-Whitney U test. Shown below are representative blots for NPPA and GAPDH. US, unstretched; S, stretched. See complete unedited blots in the supplemental material. (D) NPPA expression in iPS-CMs first transfected with siRNA against NPPA-AS1 and then subjected to 48 hours of stretch. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparisons test was used to test differences within and between groups.*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (E) RNA-Seq expression data for NPPA and NPPA-AS1 in ventricular tissue from heart failure patients (n = 42) and unused donor hearts (n = 22). ***P < 0.001 by Mann Whitney U test. (F) Correlation of NPPA and NPPA-AS1 in left ventricle and left atrium from heart failure and nonfailure donors. Pearson’s correlation coefficient and P value are shown.