Fig. 1. Summary of the experimental procedures and the characterization of the hMSC-embedded, porous RGD-Foxy5 MeHA hydrogels.
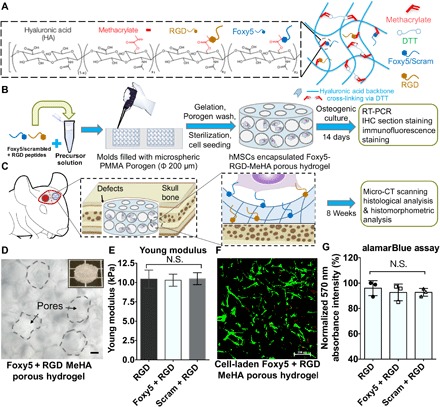
(A) Porous, Foxy5 + RGD peptide–conjugated MeHA hydrogels were developed by conjugating cysteine-containing functional peptides to MeHA molecules. (B) The porous scaffolds were used to copresent the adhesive ligand (RGD) and noncanonical Wnt5a–activating ligand (Foxy5) to synergistically induce the osteogenic lineage commitment of stem cells both in vitro and in vivo. (C) Rat MSC (rMSC)–seeded hydrogels were used to fill calvarial defects for regeneration. (D) Micrographs of the 3D porous hydrogels with Ø 200-μm pores. The inset shows the microstructure of the MeHA porous hydrogel; scale bar, 50 μm. (E) The Young modulus of the DTT-crosslinked MeHA hydrogels was verified using the Mach-1 mechanical tester. (F) The live/dead staining of the hMSCs seeded in the porous MeHA hydrogels showed the uniform distribution of the cells in the hydrogels. (G) Viable cell metabolic activity in the RGD, Foxy5 + RGD, and Scram + RGD hydrogels on day 7 of culture was characterized by alamarBlue assay. Data are shown as the means ± SD (n = 3).
