Fig. 2. BRCA1 facilitates p300-dependent p53 acetylation.
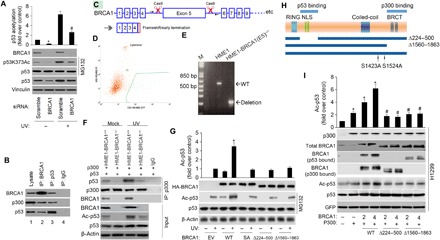
(A) p53 acetylation was decreased upon BRCA1 knockdown. MCF-7 cells were transfected with scramble or BRCA1 siRNA, followed by UV treatment (20 J/m2 for an 8-hour recovery). p53 protein level was normalized by MG132 (20 μM). p53 acetylation level on Lys373 and levels of BRCA1, p53, and vinculin were detected with specific antibodies. The data represent mean ± SD from three separate experiments. *P < 0.05 versus control; #P < 0.05 versus UV + scramble siRNA. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of BRCA1, p300, and p53 in MCF-7 cells transfected with the WT BRCA1 expression plasmid (WT BRCA1). Aliquots of cellular lysate were subjected to immunoprecipitations using anti-BRCA1, p53 antibodies, or control immunoglobulin G (IgG), followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against BRCA1, p300, or p53. (C) Schematic outline of CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing design to knock out BRCA1 exon 5. sgRNA1/2 specifically bind the introns before and after exon 5. The arrows represent location of primers for deletion PCR. Deletion of exon 5 results in frameshift, with early translational termination, mimicking a known BRCA1 pathogenic mutation. (D) Sorting for Cas9/guide transfected (GFP+) cells. (E) PCR confirms the deletion of BRCA1 exon 5 in the hTERT-HME1-BRCA1 (E5)−/− line. bp, base pairs. (F) BRCA1 KO decreases basal and UV-induced p300’s binding to total p53 and p53 acetylation. Twenty-four hours after cotransfection of the indicated plasmids, cells were treated with or without UV. Aliquots of cellular lysate were subjected to immunoprecipitations (IP) using anti-p300 antibody or control IgG, followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against p53 or p300. BRCA1, p53, and Ac-p53 were measured by immunoblotting. (G) HME1-BRCA1−/− cells were transfected with 2 μg of hemagglutinin (HA)–tagged WT, S1423A (SA), ∆224-500, and ∆1560-1863 mutant. Twenty-four hours after transfection of the indicated plasmids, cells were treated with or without UV. Cell extracts were prepared and underwent immunoblotting for the proteins as indicated, and signal intensity was quantified. Steady-state levels of transfected protein were determined by Western blot analysis using antibody against the HA epitope tag (α-HA). The data represent mean ± SD from three separate experiments. *P < 0.05 versus UV/EV. (H) Schematic diagram of BRCA1 deletion mutants used in (D). (I) H1299 cells were transfected with p53 WT and internal control GFP (lane 1) or cotransfected with c-myc–tagged p300 (lane 2) or c-myc–tagged p300 and the indicated amounts of BRCA1 WT (lanes 3 and 4), ∆224-500 mutant (lanes 5 and 6), and ∆1560-1863 mutant (lanes 7 and 8). Cell extracts were prepared (36 hours after transfection), and the levels of acetylation and total p53 protein were determined by Western blotting as described in Materials and Methods. p300 levels were determined by anti-p300 (RW128). The data represent mean ± SD from three separate experiments. *P < 0.05 versus control; #P < 0.05 versus corresponding controls in WT.
