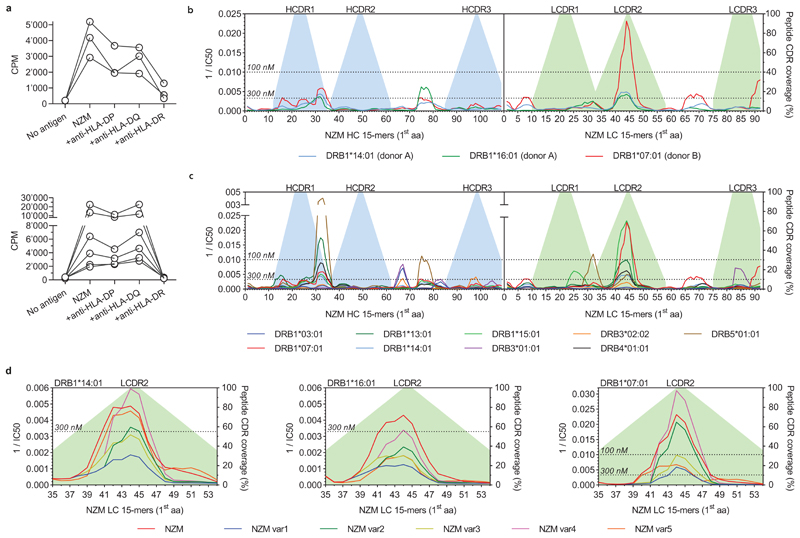
Extended Data Fig. 4. MHC restriction of NZM-reactive CD4+ T cell clones and peptide-MHC-II binding affinity predictions of NZM and deimmunized variants.
a, MHC restriction of NZM-reactive T cell clones. NZM-specific CD4+ T cell clones isolated from patient A (upper panel) and patient B (lower panel) were stimulated with antigen-pulsed autologous APCs in the absence or presence of blocking anti-MHC-II antibody (anti-HLA-DR, clone L243; anti-HLA-DQ, clone SPVL3; anti-HLA-DP, clone B7/21). Proliferation was measured on day 3 after a 16-h pulse with [3H]-thymidine, and is expressed as counts per minute (cpm). Inhibition of T cell proliferation was >80% only in the presence of the anti-HLA-DR antibody. b and c, Predicted binding affinities of all theoretical 15mer peptides derived from NZM heavy chain (HC) and light chain (LC) to HLA-DRB1 alleles carried by the two patients (b), or to a reference set of nine HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DRB3/4/5 alleles (c). The affinities are shown as reciprocal IC50 (nM) values. The dotted lines define the thresholds of high-affinity binding set at 100 nM and low-affinity binding set at 300 nM. d, Predicted binding affinities of 15mer peptides spanning the light chain CDR2 region of NZM variants to HLA-DRB1 alleles carried by patient A (DRB1*14:01 and DRB1*16:01) and patient B (DRB1*0701). The affinities are shown as reciprocal median IC50 (nM) values. The dotted lines define the thresholds of high-affinity binding set at 100 nM and low-affinity binding set at 300 nM.