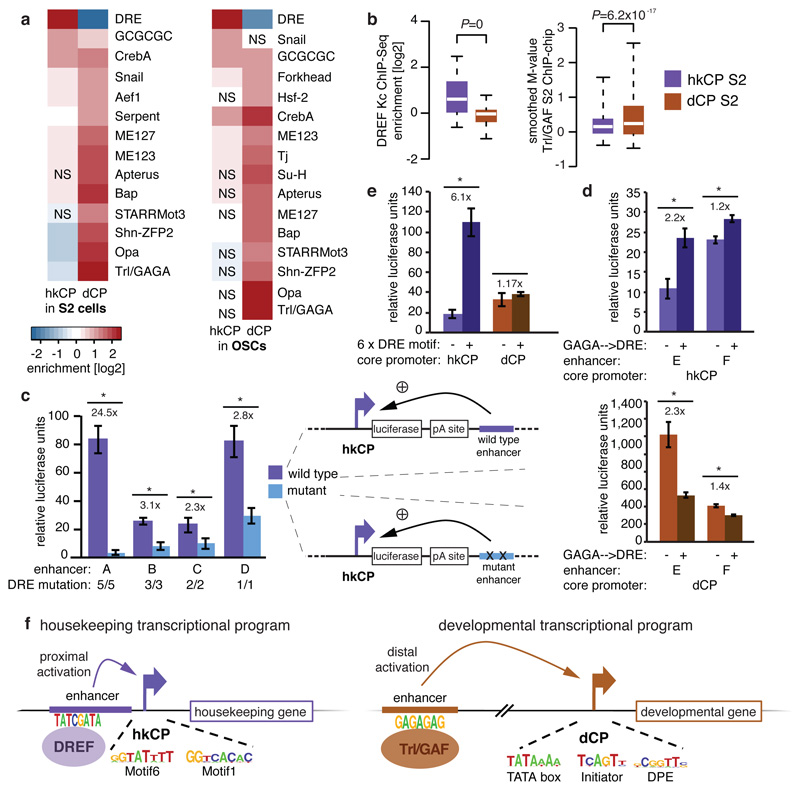
Figure 5. hkCP and dCP enhancers depend on DREF and Trl/GAF, respectively.
a-b, Motif enrichment (a) and ChIP-signals for DREF and Trl/GAF (b) in hkCP and dCP enhancers (NS: not significant [FDR-corr. hypergeometric P>0.01]; boxes: median and interquartile range; whiskers: 5th and 95th percentiles; two-sided Wilcoxon-rank-sum P-values). c, Luciferase assays (LAs) for 4 wildtype and DRE-motif-mutant hkCP enhancers (numbers: mutated motifs; error-bars: s.d. [n=3]; * P<0.005 [one-sided t-test]). d, LAs for 2 dCP enhancers (-) and Trl/GAGA→DRE-mutant variants (+) with hkCP (top) and dCP (bottom; details as in c). e, LAs for 6 DRE motifs with hkCP and dCP (details as in c). f, Model: housekeeping genes contain Motifs 1,5,6,7 and/or TCT and are activated by TSS-proximal hkCP enhancers via DREF. Regulated genes contain TATA-box, Initiator, MTE and/or DPE and are activated by distal dCP enhancers via Trl/GAF.