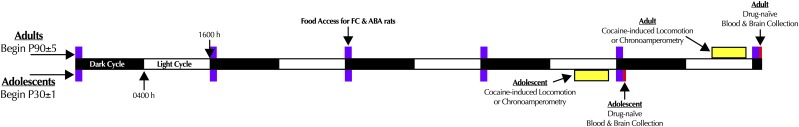
Fig. 1.
Timeline of experiments. Adult male and female rats were singly housed in cages directly adjoining running wheels at postnatal day 90 (P90, ±5 days), whereas adolescent male and female rats were housed in the same setup at P30 (±1 day). Cage control (CC) and exercise control (EC) animals had 24-hour access to food, whereas food restricted control (FC) and activity-based anorexia (ABA) animals were given access to food for 1 hour per day (purple blocks) at the onset of the dark cycle (1600 hours, 12:12 dark/light cycle, lights on at 0400 hours). Adolescents went through the paradigm for 4 days, adults for 5 days. At the end of the paradigm, animals underwent one of three endpoints: chronoamperometry (between 0900 and 1500 hours; yellow block), cocaine-induced locomotion (between 1000 and 1500 hours; yellow block), or postprandial drug-naive blood and brain collection (1700 hours, red block).