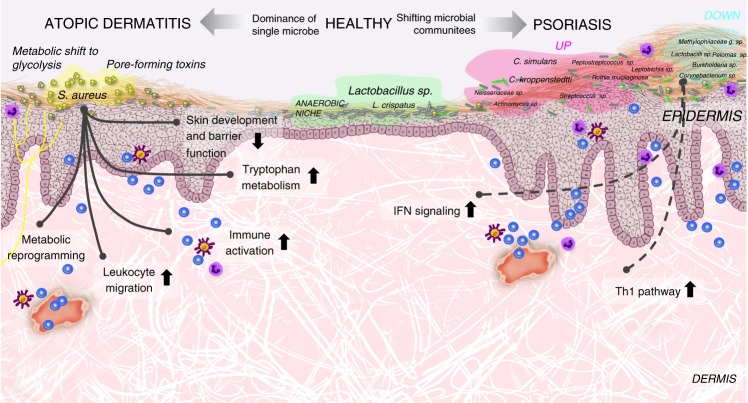
Fig. 5.
Host−microbe interaction in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. AD is characterized by overgrowth of S. aureus, and loss of microbial diversity. In AD, colonization of the skin by S. aureus is associated with dysregulation of genes involved in epithelial barrier function, immune activation, leukocyte migration, trp degradation and metabolic reprogramming. PSO is associated with multiple species, including increased colonization by C. simulans and C. kroppenstedtii, and a loss of Lactobacillus, P. acnes and Corynebacterium spp., which may play regulatory roles