Figure 6.
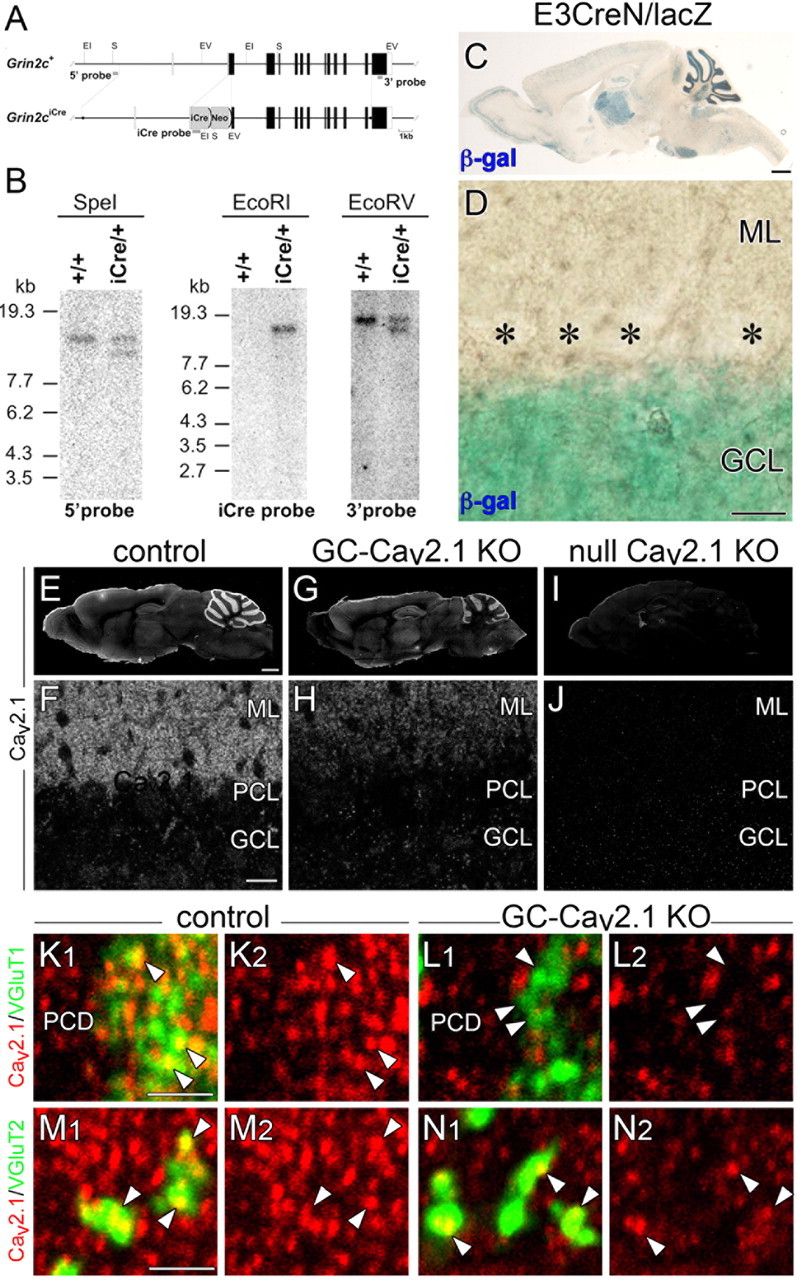
Production of mice with GC-specific Cav2.1 elimination. A, Schematic representation of the GluN2C genomic DNA (Grin2c+) and targeted genome (Grin2ciCre). The open and filled boxes indicate the noncoding and coding exons, respectively. The filled circles in the Grin2ciCre allele delineate the 5′ and 3′ termini of the targeting vector. The vector was constructed to insert an improved Cre recombinase gene (iCre) into the translational initiation site of the GluN2C gene in frame. The gray bars indicate the probes for Southern blot analysis. Two frt sequences (semicircles) are attached to remove the neomycin resistant gene (Neo). EI, EcoRI; EV, EcoRV; S, SpeI. B, Southern blot analysis of the GluN2C wild-type (+/+) and targeted (iCre/+) genome. Left, SpeI-digested genomic DNA hybridized with 5′ probe; middle, EcoRI-digested DNA hybridized with iCre probe; right, EcoRV-digested DNA hybridized with 3′ probe. Positions of DNA size markers (kilobases) are indicated on the left. C, D, Cre recombinase activity induced by E3CreN in lacZ reporter mouse. β-Galactosidase staining (blue) of parasagittal brain section (C) and cerebellar cortex (D) at P21. Asterisks indicate PC bodies. E–J, Immunofluorescence for Cav2.1 in control (E, F), GC-Cav2.1 KO (G, H), and global Cav2.1 KO (I, J) mice. Cav2.1 immunoreactivity is selectively decreased in the cerebellar cortex of GC-Cav2.1 KO mice and disappears in the brain of global Cav2.1 KO mice. K–N, Double immunofluorescence for Cav2.1 (red) with VGluT1 (green, K, L) or VGluT2 (green, M, N) in control (K, M) and GC-Cav2.1 KO (L, N) mice. Note the disappearance of Cav2.1 in VGluT1(+) PF terminals (arrowheads in K, L) but not in VGluT2(+) CF terminals (arrowheads in M, N) or shaft dendrites of PCs (PCD) in GC-Cav2.1 KO mice. β-gal, β-galactosidase; GCL, Granular cell layer; ML, molecular layer; PCL, Purkinje cell layer. Scale bars: C, E, 1 mm; D, F, 20 μm; K, M, 2 μm.
