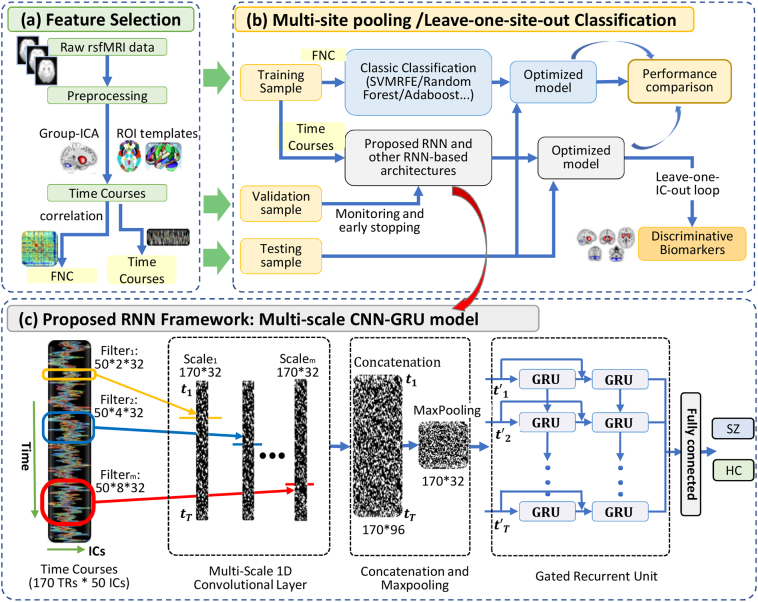
Fig. 1.
The framework of the Multi-scale RNN model in distinguishing schizophrenia patients from healthy controls. (a) Data preprocessing and feature selection. All rsfMRI data were preprocessed using the standard procedure. Time courses were then extracted using group-ICA/AAL/Brainnetome Atlas respectively. (b) The TCs/FNC data were randomly split into training, validation and testing sets. In multi-site pooling classification, all seven datasets were pooled together, and then k-fold cross-validation strategies were used for evaluating classification performance. In leave-one-site-out transfer prediction, the samples of a given imaging site were left for testing, and the samples of other sites were used for training. The performance of conventional methods (including Adaboost, Random Forest and SVM) and various RNN-based models were used for comparison. The most discriminative components were found by using leave-one-IC-out method. (c) Details of the MsRNN classification model. Three different scales convolutional filters were used for extracting of spatial features from time courses. The extracted features were then concatenated, pooling, and sent to stacked GRU module.