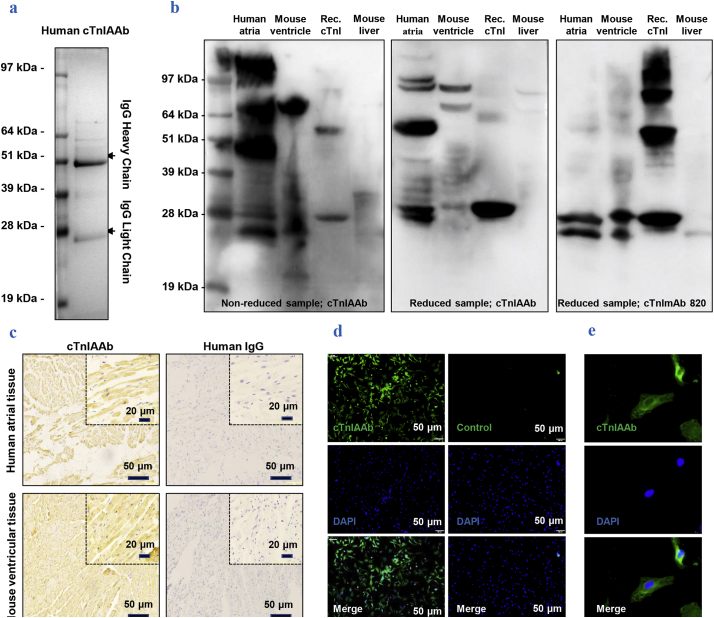
Fig. 1.
Characterization of purified human cTnIAAb.
a. Purified human cTnIAAb was subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) followed by Coomassie blue staining, which revealed two protein bands with sizes of ~51 kDa and ~28 kDa in line with the characteristic molecular weights of immunoglobulins.
b. Human cTnIAAb bound to protein lysates purified from human atria (lane 1 from left), mouse ventricles (lane 2 from left), and recombinant full-length cTnI (lane 3 from left) at the position of ~24 kDa as revealed by Western blotting. Binding to protein lysates purified from mouse liver tissue was used as a negative control (lane 4 from left). Left panel, non-reduced protein sample, anti-cTnIAAb blot; middle panel, reduced protein sample, anti-cTnIAAb blot; right panel, reduced protein sample, anti-cTnImAb blot.
c. Representative images of immunohistochemical staining showing positive staining of cTnIAAb in tissue sections prepared from human atria and mouse ventricles. Human IgG was used as a negative control. Bar = 50 μm.
d&e. Representative images showing fluorescence immunostaining of primary cultured neonatal Sprague-Dawley rat cardiomyocyte using human cTnIAAb. d, bar = 50 μm. e, bar = 20 μm. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)