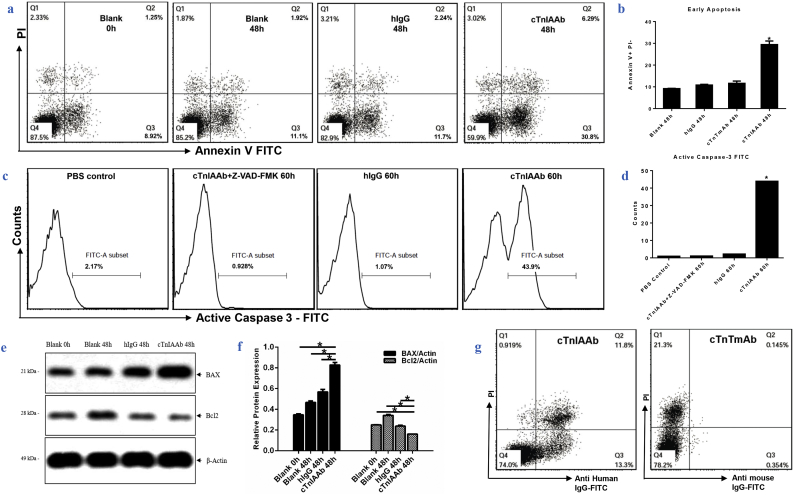
Fig. 2.
Human cTnIAAb binds membrane of cultured cardiomyocytes and causes cell apoptosis.
a&b. Flow cytometric analysis results showing that cTnIAAb treatment for 48 h triggered apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. a, Annexin V-PI staining was used for flow cytometric analysis. Representative images are shown. b, Quantification of AnnexinV/PI staining from 3 independent experiments. *p = .000 (ANOVA analysis).
c & d. Flow cytometric analysis results showing that cTnIAAb treatment for 48 h triggered apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. c, Active Caspase-3 staining was used for flow cytometric analysis. Representative images are shown. d, Quantification of Annexin-V/PI staining from 3 independent experiments. *p = .000 (ANOVA analysis).
e. cTnIAAb treatment for 48 h significantly increased expression of Bax and decreased expression of Bcl2 as revealed by immune blot analysis. β-actin was used as a loading control. Shown are representative blots of 3 independent experiments.
f. Quantification of immunoblot analysis using ImageJ software shown in e. n = 3, *p = .000 (ANOVA analysis).
g. Human cTnIAAb specifically bound to the primary cultured myocardial cell membrane as revealed by cell membrane staining and flow cytometric analysis. Shown are representative images of 3 independent experiments.