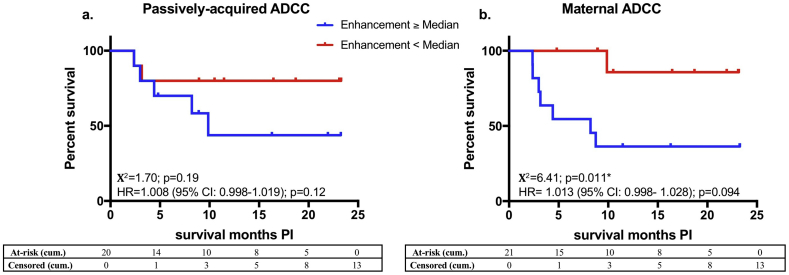
Fig. 4.
Effect of 17b-LALA-mediated ADCC enhancement on HIV-infected infant survival.
a: Kaplan-Meier survival curves between infants (N = 20) that had 17b-LALA-mediated enhancement of passively-acquired ADCC at/above the HIV-infected infant cohort median (blue line) or below the HIV-infected infant cohort median (red line) were compared by a log-rank test. b: Kaplan-Meier survival curves between infants whose mothers (N = 21) had 17b-LALA-mediated enhancement of maternal ADCC at/above the transmitting mothers cohort median (blue line) or below the transmitting mothers cohort median (red line) were compared by a log-rank test. Χ2 values and p-values are shown. The x-axis shows months survival post infection (PI). The association of 17b-LALA-mediated enhancement of passively-acquired or maternal ADCC with risk of HIV-infected infant mortality was measured by a Cox-proportional hazards model. Hazard ratios (HR), 95% confidence intervals (CI), and p-values are shown on the graphs. Statistical significance was defined as p < 0·05 (*). Cumulative (cum.) number of infants at-risk or censored by the end of each month on the x-axis are shown in the tables. Data from individual biological replicates from one maternal sample and one infant sample that were below the limit of detection were excluded from the analysis as described in the Materials and Methods. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)