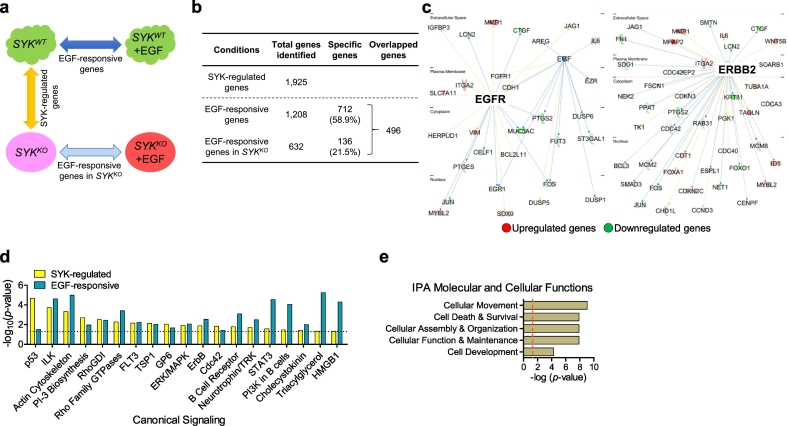
Fig. 3.
Alteration of the EGF-regulated transcriptome by SYK knockout. (A) The design and comparative analyses examining differentially expressed genes between OVISE SYKWT and syngeneic SYKKO cells in the presence or absence of EGF using RNA-seq. EGF-responsive genes are obtained from comparing SYKWT cells with and without addition of EGF (50 ng/mL). This comparison is extended to SYKKO cells to derive EGF-responsive genes in SYKKO condition, while comparison between SYKWT and SYKKO (in the absence of EGF) results in genes that are regulated by SYK. (B) Numbers of differentially expressed genes (FDR <0.01) identified as “SYK-regulated genes”, “EGF-responsive genes” or “EGF-responsive genes in SYKKO”. (C) Ingenuity Pathway Analysis showing transcriptional network of EGFR-regulated and ERBB2-regulated genes identified among the genes that were differentially expressed between SYKWT and SYKKO cells. Upregulated genes are shown in red, and downregulated genes in green. (D) Top canonical signaling pathways that are shared between SYK-regulated and EGF-responsive genes. (E) Function-based analysis of the 712 “SYK-dependent” genes. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)