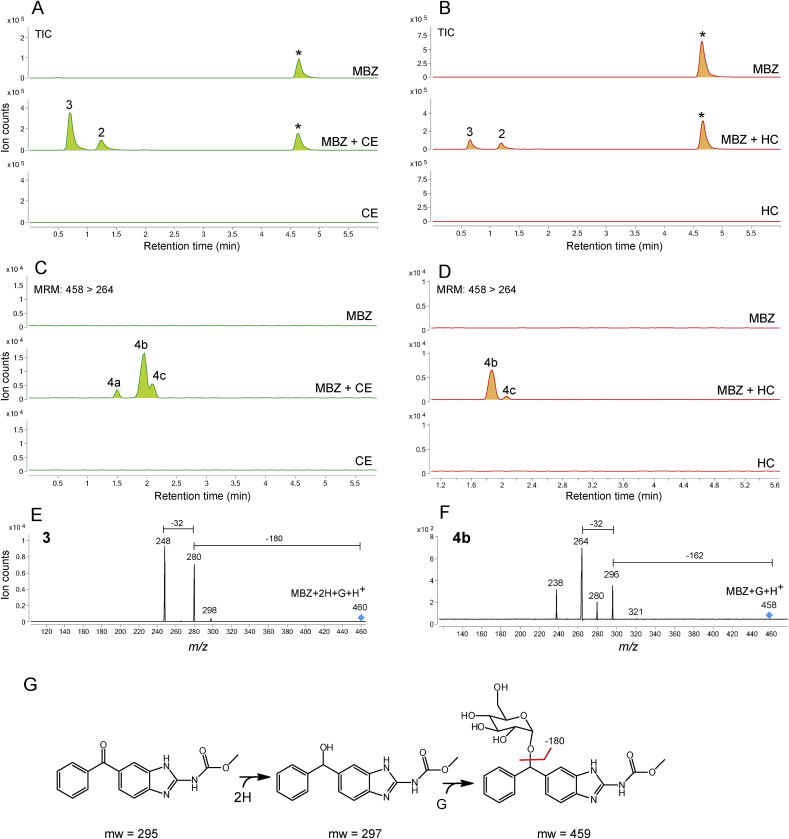
Fig. 2.
Chromatograms are the result of product Total Ion Current (TIC) or multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) of mebendazole (MBZ) parental drug and its metabolites identified in the supernatant of cultures of C. elegans benzimidazole resistant allele CB3474 ben-1(e1880)III (shown in green) or of adult H. contortus drug sensitive MHco3(ISE) allele (shown in orange). The first (top) chromatogram corresponds to the culture containing benzimidazole but no nematodes, the second chromatogram corresponds to the culture containing either C. elegans or H. contortus respectively, exposed to the benzimidazole, and the third chromatogram corresponds to the control culture containing C. elegans or H. contortus but with no benzimidazole. C. elegans was exposed to 56.5 μM BZ for 3 days, and H. contortus was exposed to 10 μM BZ for 16 h respectively. A. TIC chromatogram of C. elegans exposed to mebendazole (MBZ), B. TIC chromatogram of H. contortus exposed mebendazole (MBZ), C. Multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) chromatogram of C. elegans exposed to mebendazole (MBZ), D. Multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) chromatogram of H. contortus exposed to mebendazole (MBZ). Metabolites and their LC-MS/MS fragmentation patterns identified in supernatant of the MBZ-treated C. elegans or adult H. contortus cultures. These fragmentation patterns were extracted from a Total Ion Current (TIC) or multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) and resulted from a fragmentor setting of 150 V and a collision energy of 30eV. E. Metabolite 3 and its LC-MS/MS fragmentation pattern. F. Metabolite 4b and its LC-MS/MS fragmentation pattern. Two diagnostic daughter ions derived from the m/z 428 ion were m/z 234 and m/z 266 of the fragmentation data. G. Proposed sequential reaction of reduction and O-glycosylation to the phenyl ketone moiety in MBZ. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article).