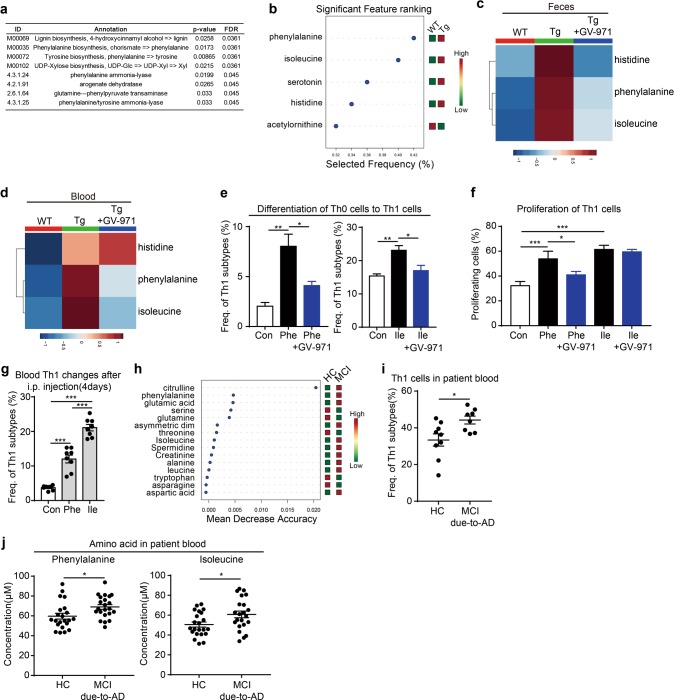
Fig. 5.
GV-971 inhibits neuroinflammation by harnessing amino acid metabolism. a Pathway enrichment analysis of faecal metabolites in 7-month-old 5XFAD (Tg) mice with or without GV-971 treatment (100 mpk) using MBROLE (n = 6–8). A partial ist of the enrichment results is presented with KEGG modules and KEGG enzyme interactions which have been screened using a criterion of FDR-adjusted P-value < 0.05. b Lists of the most important blood amino acids of the random forest model ranked from most to least important between WT (2 m-9 m) and Tg (2 m-9 m) group from a ROC curve analysis. Red indicated high concentration, green indicated low concentration. (n = 30 for WT, n = 26 for Tg). c Changes in histidine, phenylalanine and isoleucine levels in the feces of WT, 5XFAD mice (Tg), and GV-971-treated Tg mice (100 mpk) (n = 6–11) at 7-month old. Colours in the heatmap indicate relative metabolite levels; red indicates metabolites that are upregulated, and blue indicates metabolites that are downregulated. d Changes in histidine, phenylalanine and isoleucine levels in the blood of WT, 5XFAD mice (Tg), and GV-971-treated Tg mice (100 mpk) (n = 6–7) at 7-month old. Colours in the heatmap indicate relative metabolite levels. Red indicates metabolites that are upregulated, and blue indicates metabolites that are downregulated. e The effects of GV-971 on the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells (Th0 cells) to Th1 cells induced by phenylalanine and isoleucine in vitro. Naïve CD4+ T cells were cultured for 5 days with/without GV-971 in the presence of phenylalanine (1 mM) or isoleucine (1 mM). The frequency of Th1 (CD4+IFN-γ+) cells was tested by flow cytometry (see Materials and methods). GV-971 was used at a final concentration of 100 µg/mL. The data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (mean ± SEM); n = 3 replicates per group, one of three replicated results was represented. Left, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA (F (2, 6) = 15.64). Right, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA (F (2, 6) = 10.35). f The effects of GV-971 on the proliferation of Th1 cells induced by phenylalanine and isoleucine. Th1 cells were stained with CellTrace and cultured for 4 days with/without GV-971 in the presence of phenylalanine (1 mM) and isoleucine (1 mM). The density of CellTrace fluorescence in Th1 (CD4+IFN-γ+) cells was tested by flow cytometry (see Materials and methods). GV-971 was used at a final concentration of 100 µg/mL. The data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (mean ± SEM), n = 3 replicates per group, one of three replicated results was represented. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA (F (4, 9) = 28.34). Phe, phenylalanine; Ile, isoleucine. g Frequency of blood Th1 cell changes in C57 mice after 4-day intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of phenylalanine and isoleucine (n = 8). ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA (F (2, 21) = 101.8). h Random forest classification of amino acid changes in healthy controls (HC) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) due to AD patients. The amino acids are ranked by mean decrease in classification accuracy (first cohort, n = 9 for MCI due to AD, n = 18 for HC). Red indicated high concentration, green indicated low concentration. i Frequency of Th1 cells in the blood of healthy controls (HC) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) due to AD patients (first cohort, n = 8 for MCI due to AD, n = 9 for HC). *P < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. j Levels of phenylalanine and isoleucine in the blood of healthy controls (HC) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) due to AD patients (second cohort, n = 22 for both groups). *P < 0.05 by Student’s t-test