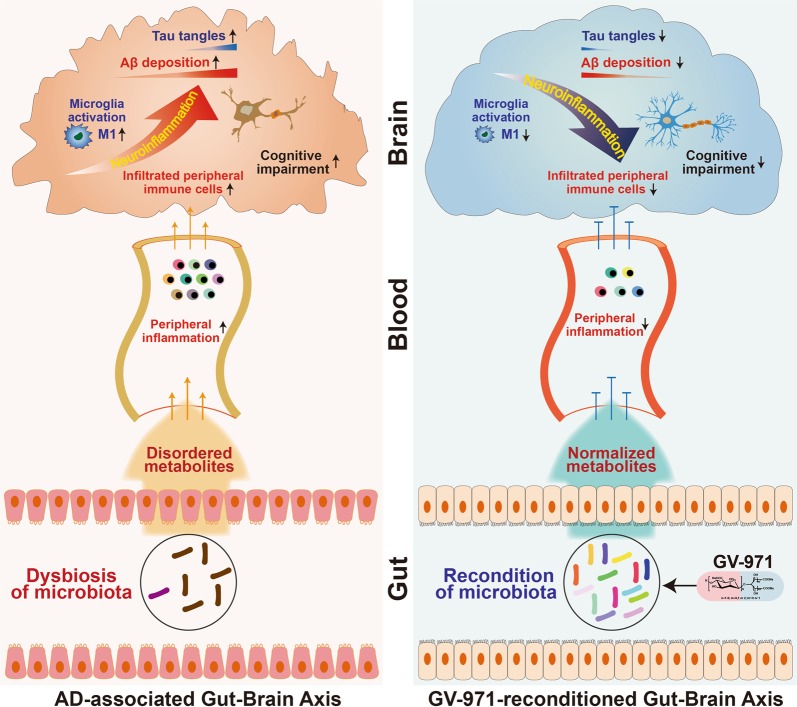
Fig. 6.
Schematic diagram of gut-brain axis in AD progression and the intervention strategy. Along with Aβ deposition and tau phosphorylation, the alteration of the gut microbiota during AD progression causes metabolic disorder. The abnormal metabolites production provoke peripheral inflammation, increases the brain infiltration of immune cells which crosstalk with M1 microglial cells in the brain, resulting in pathological neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment (left panel). Oral administration of GV-971 reconditions the gut microbiota, normalizes disordered metabolites, reduces the peripheral immune cell infiltration to the brain, resolves neuroinflammation, and reduces Aβ deposition and tau phosphorylation, leading to ultimate improvement of cognitive functions (right panel)