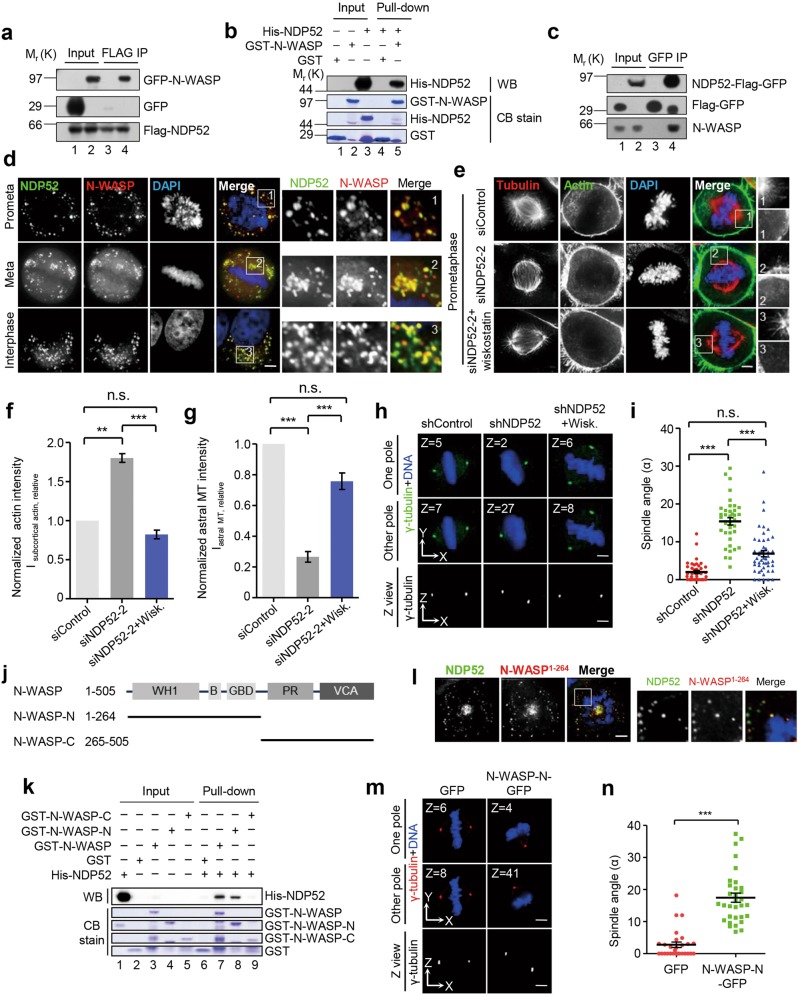
Fig. 4.
NDP52 inhibits premature formation of subcortical F-actin ring via N-WASP a HEK293T cells co-expressing 3 × Flag-NDP52 and GFP-N-WASP were lysed, immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG beads and analyzed by Western blotting. Lanes 1–2 annotate the input while lanes 3 and 4 mark immunoprecipitates of Flag-NDP52. See also Supplementary Fig. S4. b Pull-down assay with GST-N-WASP and His-NDP52. GST-N-WASP affinity matrix was used to bind His-NDP52. The binding fractions were subjected to SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue or analyzed by Western blotting. Lanes 1–3 represent inputs which contain GST, GST-N-WASP and His-NDP52 protein, respectively, while lanes 4 and 5 mark pull-down fractions which contain proteins bound to GST or GST-N-WASP. Note that His-NDP52 binds to GST-N-WASP (lane 5) but not GST (lane 4). See also Supplementary Fig. S4. c The NDP52–3 × Flag-GFP knock-in HeLa cells synchronized by nocodazole treatment were lysed, and the clarified cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with GFP trap beads followed by Western blotting analyses. In negative control group, HeLa cells expressing 3 × Flag-GFP were used. Lanes 1–2 annotate the input while lanes 3 and 4 represent immunoprecipitates of NDP52-Flag-GFP and Flag-GFP, respectively. d Co-localization of NDP52-GFP and N-WASP-mCherry in mitosis and interphase. HeLa cells expressing NDP52-GFP and N-WASP-mCherry were synchronized with monastrol (prometaphase) or MG132 (metaphase) after release from the thymidine treatment. Scale bar, 5 μm. e Immunofluorescence staining for α-tubulin and F-actin in NDP52-depleted HeLa cells (siNDP52–2) with and without the treatment of wiskostatin. Scale bar, 5 μm. f Quantification of subcortical actin fluorescence intensity (Isubcortical actin, relative) in above-mentioned cells (n = 6 for each group). Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Student’s t-test, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; n.s., no significant difference. g Quantification of astral microtubule fluorescence intensity (Iastral MT, relative) in above-mentioned cells (n = 6 for each group). Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Student’s t-test, ***P < 0.001; n.s., no significant difference. h Representative immunofluorescence images of z-sections (0.2 μm per stack) with maximum spindle pole intensity in NDP52-depleted HeLa cells with and without the treatment of wiskostatin. Scale bar, 5 μm. See also Supplementary Fig. S4. i Scatter plots showing the spindle angles in indicated HeLa cells (n = 40, shcontrol; n = 38, shNDP52; n = 48, shNDP52 + wiskostatin). Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Student’s t-test, ***P < 0.001; n.s., no significant difference. j Schematic representation of N-WASP and deletion mutants. Abbreviations are as follows: WH1, WASP homology 1 domain; B, basic domain; GBD, GTPase-binding domain; PR, proline-rich domain; VCA, verprolin-cofilin-acidic domain. Note that VCA domain binds actin and promotes actin polymerization. k Identification of NDP52-binding domain within the N-WASP protein by pull down assay. Lanes 1–5 represent inputs which contain GST, GST-N-WASP (full-length and truncations) and His-NDP52 protein, respectively, while lanes 6–9 mark the pull-down fractions which contain proteins bound to GST (negative control) or GST-N-WASP. Note that N-terminal N-WASP protein interacts with NDP52 directly (lane 8). l N-WASP-N-mCherry co-localizes with NDP52-GFP in mitosis. HeLa cells expressing NDP52-GFP and N-WASP-N-mCherry were synchronized with monastrol after release from the thymidine treatment. Scale bar, 5 μm. m Representative immunofluorescence images of z-sections (0.2 μm per stack) with maximum spindle pole intensity in HeLa cells overexpressing GFP or N-WASP-N-GFP. Scale bar, 5 μm. See also Supplementary Fig. S4. n Scatter plots showing the spindle angles in indicated HeLa cells (n = 26, GFP; n = 32, N-WASP-N-GFP). Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Student’s t-test, ***P < 0.001