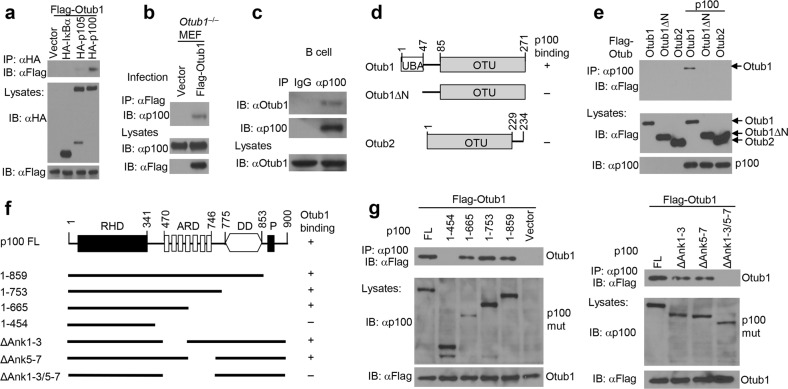
Fig. 1.
Identification of Otub1 as a p100-binding protein. a Co-immunoprecipitation (coIP) analysis of p100/Otub1 binding (upper) and direct immunoblot analysis for monitoring protein expression (lower) using whole-cell lysates of HEK293 cells transfected with Flag-tagged Otub1 along with either an empty vector or expression vectors encoding the indicated IκB proteins. b Whole-cell lysates were prepared from Otub1–/– MEFs reconstituted with either an empty vector or Flag-Otub1 and subjected to coIP to detect Otub1 binding to endogenous p100 (upper) or direct immunoblot assays (lower). c CoIP analysis of endogenous Otub1/p100 interaction in whole-cell lysates of untreated wild-type splenic B cells. IgG pulldown was used as a negative control for p100 IP. d, e A schematic picture depicting the domains of Otub1 and Otub2 (d) and coIP analysis of p100/Otub1 interaction using whole-cell lysates of HEK293 cells transfected with the indicated expression vectors (e). f, g A schematic picture depicting the domains of p100 and its mutants (f) and coIP analysis of Otub1 interaction with p100 mutants using whole-cell lysates of HEK293 cells transfected with the indicated expression vectors (g, upper). Cell lysates were also subjected to direct immunoblotting to monitor expression of p100 mutants (p100 mut) and Otub1 (lower)