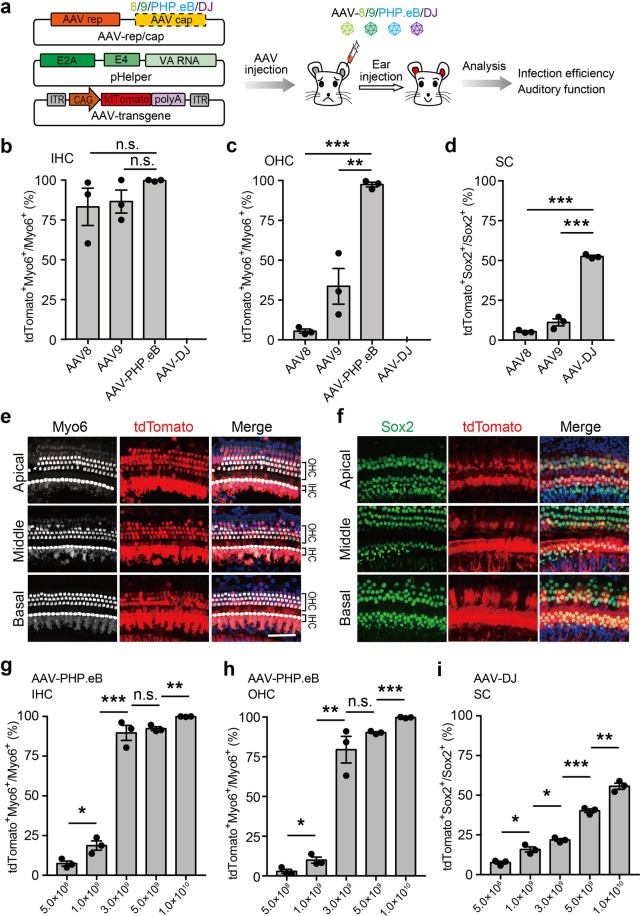
Fig. 1. Infection efficiencies of different adeno-associated virus (AAV) variants for hair cells (HCs) and supporting cells (SCs).
a Schematic overview of infection screening in hair cells and supporting cells using different subtypes of AAVs. Different subtypes of AAVs (AAV-8/9/PHP.eB/DJ) were packaged and injected into the cochlea of P1 Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice. The injected cochlea regions were dissected for immunostaining and phenotype analysis at 3 weeks post injection. b–d Infection efficiencies of different AAV subtypes measured by the percentage of tdTomato+ cells in inner HCs (IHCs) (b), outer HCs (OHCs) (c), and SCs (d). Results were obtained from three animals and are presented as mean ± SEM. For each animal, HC and SC infection was quantified at six different locations along the cochlea: two at the apex, two at the middle turn, and two at the cochlear base. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, unpaired Student’s t test. e, f Representative immunofluorescence images of HCs and SCs in cochlea sections injected with AAV-PHP.eB or AAV- DJ at 3 weeks post injection. Myo6, HC marker; Sox2, SC marker; tdTomato, transfected cells. Scale bar, 50 μm. g–i Infection efficiencies of different doses of AAV-PHP.eB and AAV-DJ in IHCs (g), OHCs (h) and SCs (i). Results were obtained from three animals and are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001; n.s., no significance; unpaired Student’s t test