Fig. 3.
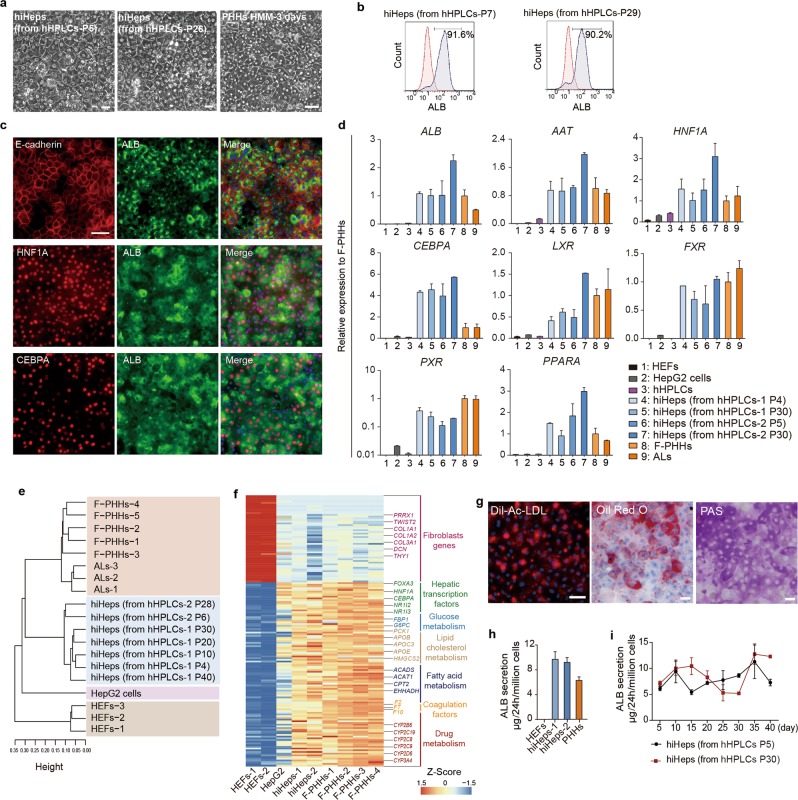
hiHeps recapitulate mature hepatocyte phenotypes as PHHs in vitro. a Bright field images show the polygonal morphology of hiHeps derived from hHPLCs-P5 and hHPLCs-P26 and freshly isolated primary hepatocytes cultured in HMM for 3 days. b Flow cytometry analysis of ALB positive cells in hiHeps derived from hHPLCs-P7 and hHPLCs-P29. c Co-immunofluorescence staining of E-cadherin, HNF1A and CEBPA with ALB in hiHeps derived from hHPLCs-P5. d RT-qPCR analysis of major mature hepatocyte functional genes in HEFs (n = 3), HepG2 cells (n = 2), hHPLCs (n = 2), hiHeps derived from hHPLCs at different passages (n = 2), F-PHHs (n = 5) and ALs (n = 4). Relative expression was normalized to F-PHHs. e Hierarchical clustering of global gene expression of HepG2 cells, HEFs, F-PHHs, ALs and hiHeps derived from hHPLCs at different passages. f Heatmaps of fibroblast genes, hepatic transcription factors and functional hepatocyte genes involved in glucose metabolism, lipid cholesterol metabolism, fatty acid metabolism, coagulation and drug metabolism in HEFs, hiHeps and F-PHHs. g Essential hepatic functions in hiHeps: LDL uptake (left), Oil Red O staining (middle) and PAS staining (right). h ALB secretion in HEFs, hiHeps and PHHs analyzed by ELISA. n = 3. i Dynamic monitoring of ALB secretion in hiHeps and PHHs analyzed by ELISA. n = 3. For all measurements, ‘n’ represents the number of biological replicates. The scale bars represent 50 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM