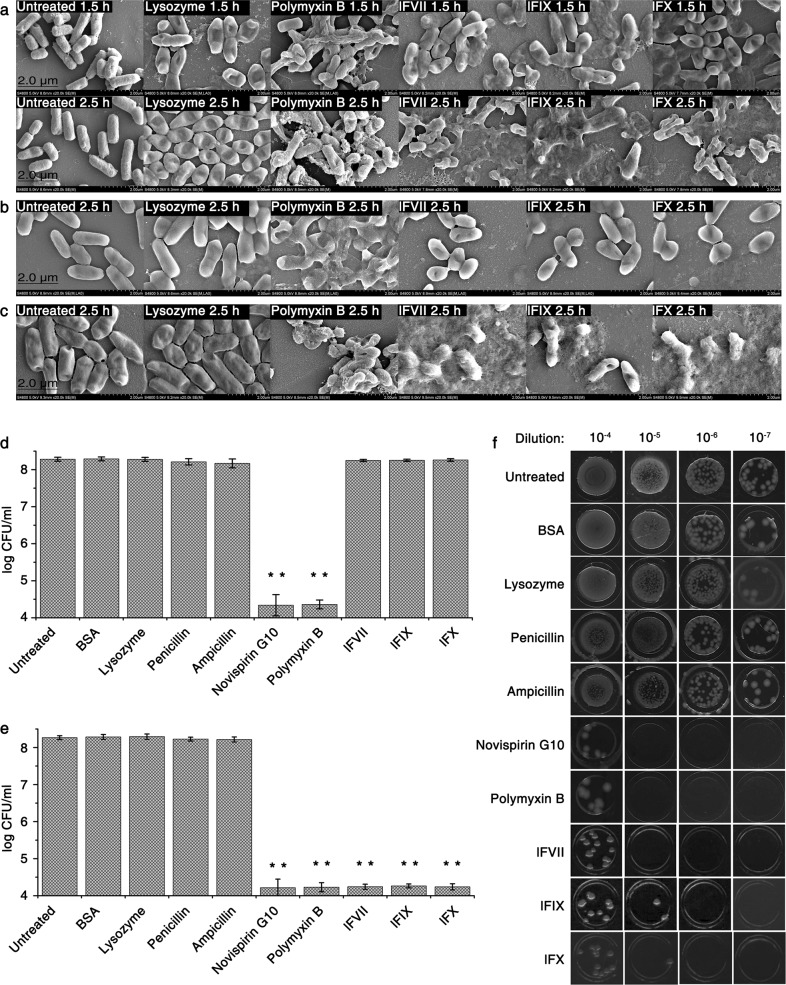
Fig. 2.
LCs damage bacterial cell envelope without disturbing its biosynthesis. a–c SEM images of E. coli DH5α following treatment with different agents under different culture conditions. Bacteria were incubated with the indicated agents in LB for 1.5 or 2.5 h (a), in hypertonic LB for 2.5 h (b) or in hypotonic LB for 2.5 h (c), and then the pictures were captured using SEM. d–f Effects of the LCs on the survival of starving E. coli DH5α. Bacteria were treated with the indicated agents in hypertonic (d) or hypotonic TBS (e) for 4 h at 37 °C. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). **P < 0.01, significantly different from the untreated cells. Bacteria treated in hypotonic TBS, which were the same as those tested in e, were also spotted on hypotonic LB solid medium following a serial dilution (f). Untreated bacteria were included in all experiments. The final concentrations of different agents are listed as follows: lysozyme, 50 μg/mL; polymyxin B, 10 μg/mL; lFVII, 100 μg/mL (4× MIC against E. coli DH5α); lFIX, 100 μg/mL (4× MIC against E. coli DH5α); lFX, 100 μg/mL (4× MIC against E. coli DH5α); BSA, 100 μg/mL; penicillin, 100 μg/mL; ampicillin, 250 μg/mL; novispirin G10, 10 μg/mL