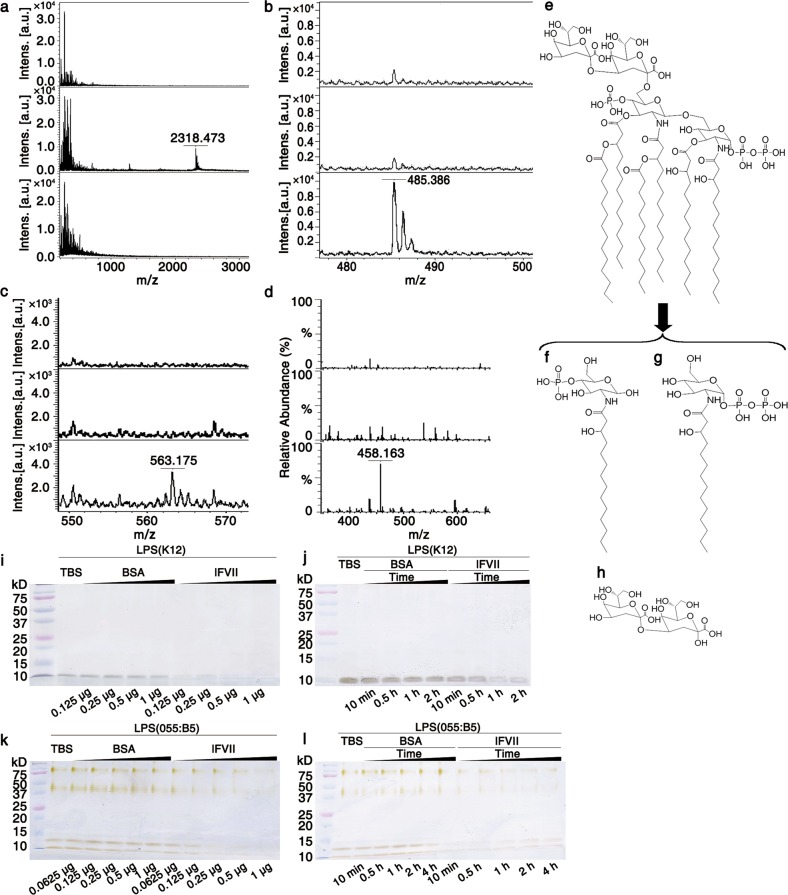
Fig. 3.
lFVII-triggered LPS hydrolysis. a–d lFVII-triggered E. coli K12 LPS hydrolysis detected by MALD/TOF-MS (a–c) and ESI-MS (d). lFVII in buffer (150 µg/mL) (top); LPS in buffer (625 µg/mL) (middle); LPS (625 µg/mL) incubated with lFVII (150 µg/mL) in buffer (bottom). e–h Structures of 6-Kdo-(1-bis-4′-mono)-phosphorylated-hexaacylated-lipid A (the peak with an m/z value of 2318.473 in a, e) and the LPS hydrolysates produced after lFVII treatment (f–h). i–l lFVII degrades the LPS from E. coli K12 (i, j) and E. coli 055:B5 (k, l). Twenty micrograms of E. coli K12 LPS or 10 μg of E. coli 055:B5 was tested at 37 °C per reaction; the dose of protein (i, k) and the treatment time (j, l) were increased as indicated; the treatment time in i and k was 2 h, and the protein doses in j and l were 0.25 μg and 1 μg per reaction, respectively. Separated LPS samples on Tricine-SDS-PAGE were examined by silver staining