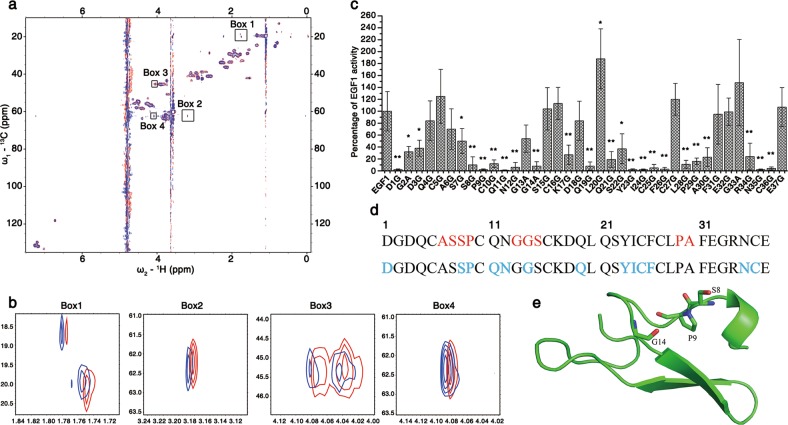
Fig. 5.
Residues critical for the antibacterial activity of lFVII. a, b lFVII EGF1-LPS interaction detected by NMR chemical shift perturbation experiments. Two-dimensional 1H–13C HSQC spectra were recorded in the presence of different molar ratios of EGF1 to LPS (Red, 1:0, Blue, 1:0.1) (a). When the molar ratio between EGF1 and LPS reached 1:0.25, all the signals disappeared (data not shown), possibly due to molecular aggregation. Four different regions of the spectra named Boxes 1–4 were enlarged in b. The peaks in Box 1 showed a 13C chemical shift value (CSV) of ~20 ppm, which clearly indicates that the signal comes from the Cβ nucleus of an alanine; the peak in Box 2 showed a 13C CSV of ~62 ppm, and a 1H CSV of 3.2 ppm, which could possibly arise from Cβ–Hβ of a serine or threonine (since there is no threonine in the primary sequence of EGF1, it has to be serine); the peaks in Box 3 showed a 13C CSV of ~20 ppm, which directly points to a glycine residue; the peak in Box 4 showed a 13C CSV of ~62 ppm, and a 1H CSV of 4.1 ppm, which could possibly arise from Cα–Hα of a proline or valine (it could be proline as there is no valine in the EGF1 sequence). c Antibacterial activities of a serial EGF1 mutants towards E. coli DH5α. To produce EGF1 mutants, alanine was introduced to replace the glycine in EGF1 sequence, and glycine was introduced to replace the amino acids other than glycine. The antibacterial activities were determined by MIC measurement, and the data were presented as a percentage of the activity of wild-type EGF1 (EGF1) and as means ± SD (n = 5 independently purified protein samples). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, significantly different from the EGF1. The value of <10% was considered as a significant reduction in antibacterial activity. d Primary sequence of EGF1 domain of FVII. Residues that were perturbed in the NMR titration assay are shown in red, and the residues exhibiting functional importance in antibacterial assay are colored in blue. e Crystal structure of the EGF1 domain of FVII (PDB ID: 1QFK).50 Side-chains of the potential LPS-interacting residues were displayed. The crystal structure of EGF1 domain used here is generally similar to its solution structure (PDB ID: 1BF9 and 1F7M) (Supplementary information, Fig. S6f)