Fig. 3.
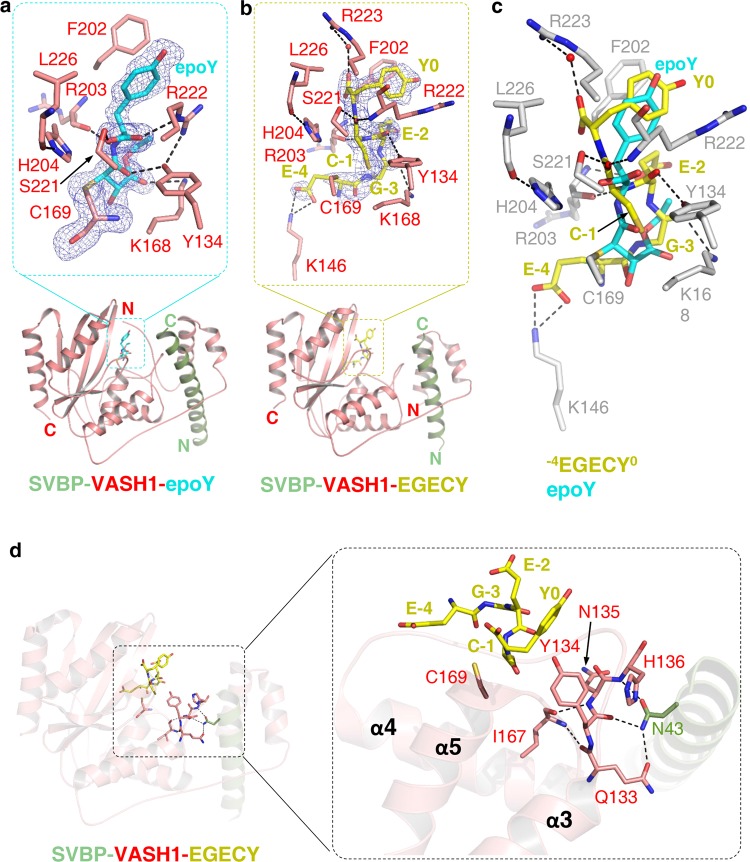
Molecular mechanism of tubulin detysosination by VASH1. a The structure of VASH157–306 (red) in complex with SVBP1–52 (green) and epoY (cyan). epoY and epoY-interacting residues of VASH1 are shown in sticks. The |Fo|–|Fc| difference electron density map of epoY is contoured at 3.0 σ and is shown as blue mesh with epoY deleted prior to one round of refinement. b The structure of VASH170–306 (red) in complex with SVBP3–49 (green) and −7GEEEGECY0 peptide (yellow). Peptide and peptide-interacting residues of VASH1 are shown in sticks. Only five residues of the peptide (−4EGECY0) are visible in the structure. The |Fo|–|Fc| difference electron density map of the peptide is contoured at 3.0 σ and is shown as blue mesh with the peptide deleted prior to one round of refinement. c Superposition of epoY-bound and −7GEEEGECY0-bound SVBP-VASH1 structures. epoY, −4EGECY0, and VASH1 residues involved in peptide binding are shown in cyan, yellow, and gray sticks, respectively. d Allosteric regulatory role of SVBP. SVBP, VASH1 and the peptide are colored in the same way as shown in b. The 133QYNH136 motif, Ile167 and Cys169 of VASH1, Asn43 of SVBP and peptide residues are shown in sticks.