Fig. 1.
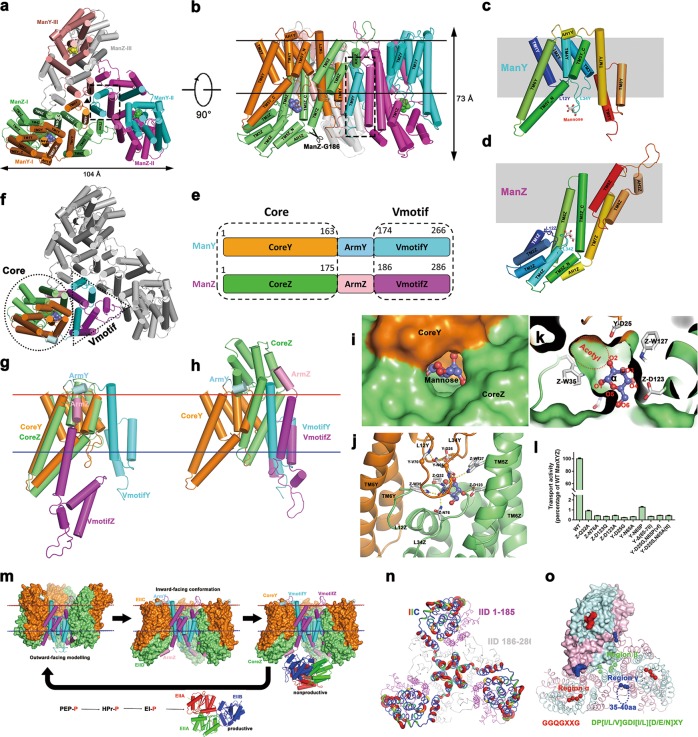
Cryo-EM structure study of ManYZ complex. a, b Cartoon representation of the ManYZ structure is shown in two perpendicular views. The scissor in b indicates the maximum C-terminal truncation of ManZ, at which the penetration of λ DNA across the inner membranes is only slightly affected. c, d ManY c and ManZ d are cartoon-represented and rainbow-colored. e Color-coded domain architecture of ManY and ManZ. The same color scheme is used in all structure figures below if not specified elsewhere. f The structure of ManYZ complex with domains color-coded as aforementioned. VmotifY and VmotifZ interlocked to form Vmotif domain, whereas CoreY and CoreZ give rise to Core domain. g The structure alignment of ManY and ManZ based solely on Core domain. ArmY and ArmZ separate, which induces VmotifY and VmotifZ in the different orientation. h Structure alignment of ManY and ManZ based on Vmotif domain. i, j Surface representation of substrate-binding pocket. k Mannose is shown as sticks with carbon in slate and oxygen in red. Protein–mannose interactions are marked as dotted lines. l The proteoliposome assay of 15 min D-[2-3H]-mannose uptake for ManYZ variants. Details of the experiments are described in the ‘Materials and methods’ section in Supplementary information. Error bars are s.e.m of three independent measurements. m The elevator mechanism of mannose transportation by ManXYZ complex. Outward-facing model constructed according to the symmetrical roles of ManY and ManZ. CoreY, VmotifY, CoreZ and VmotifZ domains are colored in orange, cyan, lime and magenta, respectively. EIIAs are colored in red and green, and EIIB in blue. n The putty representation of non-conservation of ManY/IIC between E. coli and K. pneumoniae, which is the major specificity determinant for bacteriophage λ infection, is shown and colored in rainbow from blue to red. The residues 186–286 of ManZ/IID are colored gray to indicate that their truncation does not affect the penetration of lambda DNA. However, the residues 1–186 of ManZ, although not specificity determinant, are colored in magenta and necessary for the stability of the whole complex. o Three regions of the mannose phosphotransferase system (α: red, β: green, and γ: blue) are responsible for specific targeting by class IIa bacteriocins