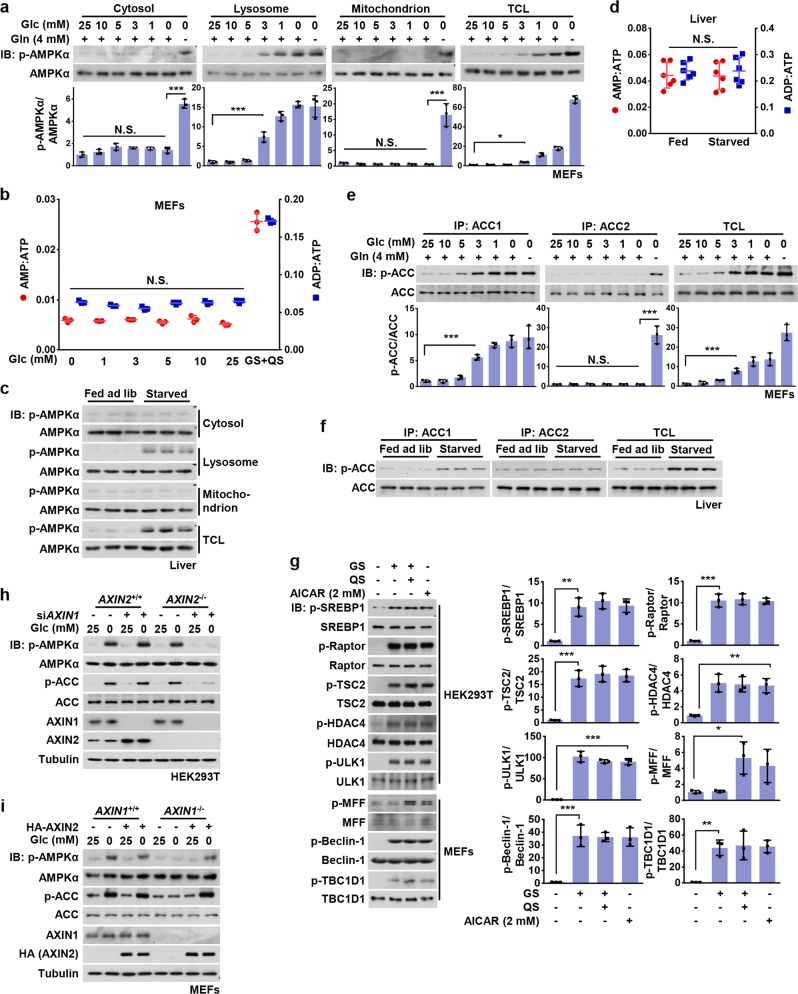
Fig. 1. Basal AMP Is Sufficient for Activation of the Lysosomal Pool of AMPK.
a Low glucose exclusively activates the lysosomal pool of AMPK in MEFs. MEFs were grown in full medium and then switched to DMEM containing reduced concentrations of glucose for 2 h, or to DMEM lacking both glucose and glutamine (starvation for glucose plus glutamine, GS + QS). Cytosolic, lysosomal, and mitochondrial fractions were prepared following the methods described in “Materials and Methods”. Fractions were then subjected to analysis of p-AMPKα and p-ACC by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies, followed by densitometry analysis. Statistical analysis results were shown in mean ± SD; ***p < 0.001, *p < 0.05, N.S., not significant by ANOVA, n = 3. b AMP:ATP and ADP:ATP ratios are not changed in MEFs in low glucose. Adenylate nucleotide ratios in MEFs treated as in a were measured by CE-MS. Results are mean ± SD; N.S., not significant by ANOVA, n = 3. c Starvation-induced AMPK activation in liver takes place on lysosome. Mice were fed ad libitum or starved for 16 h, followed by fractionation of cytosol, lysosomes and mitochondria from liver homogenates, and subsequent immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. d AMP/ATP and ADP/ATP ratios are unchanged in the liver of starved mice. Mice were fed or starved as in (c), freeze-clamped liver samples prepared, and AMP/ATP and ADP/ATP ratios measured by CE–MS. Results are mean ± SD, n = 6; N.S., not significant by Student’s t-test. e, f ACC1, but not ACC2, is phosphorylated in MEFs starved for glucose or in the liver of starved mice. MEFs were glucose starved or severely starved as in a, while mice were fed or starved as in c. Endogenous ACC1 and ACC2 in MEFs (e) or mice livers (f) were individually immunoprecipitated, followed by immunoblotting. Statistical analysis data of experiments in e were shown in mean ± SD; ***p < 0.001, N.S., not significant by ANOVA, n = 3. g Phosphorylation of SREBP1c, TSC2, Raptor, HDAC4, ULK1, Beclin-1, and TBC1D1, but not MFF, is observed in low glucose. HEK293T cells or MEFs were incubated in DMEM medium with (25 mM) or without glucose for 2 h, followed by analysis of phosphorylation levels of AMPK substrates as indicated. Statistical analysis data were shown in mean ± SD; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, by ANOVA, n = 3. h AXIN1 and AXIN2 are functionally equivalent in the lysosomal pathway of AMPK activation in HEK293T cells. AXIN2−/− HEK293T cells and its wildtype control were infected with lentivirus expressing siRNA against AXIN1. Cells were starved for glucose for 2 h and then lyzed, followed by immunoblotting. i Re-introduction of AXIN2 into AXIN1−/− MEFs restores glucose starvation-induced AMPK activation. AXIN1−/− MEFs (and its wildtype control) were infected with lentivirus expressing HA-tagged AXIN2. Cells were then starved for glucose for 2 h, followed by immunoblotting. Experiments in this figure were performed three times, except d and i twice. See also Supplementary information, Fig. S1