FIG 1.
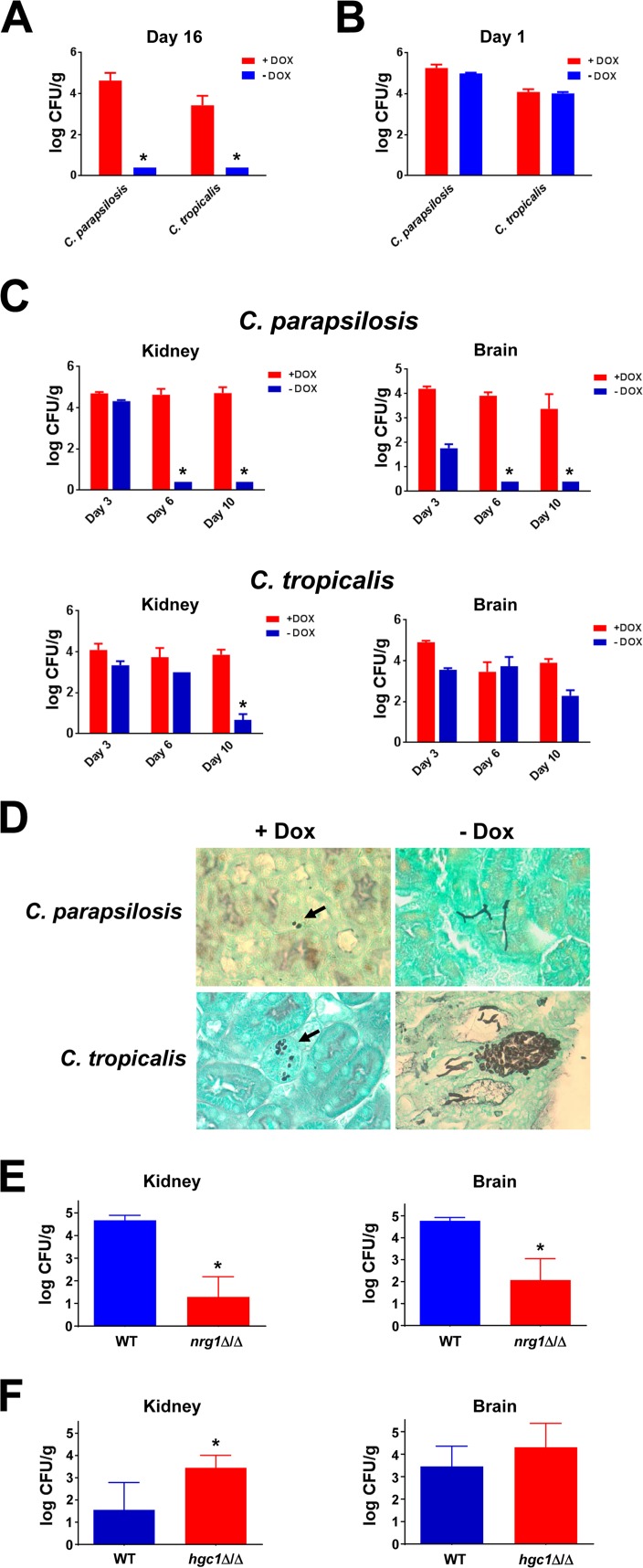
Filamentation is associated with reduced fungal burden of C. tropicalis and C. parapsilosis in a mouse model of systemic candidiasis. (A) C. tropicalis (4 × 104 CFU) and C. parapsilosis (4 × 106 CFU) tetO-UME6 strains were used to inoculate female BALB/c mice (6 to 8 weeks old) by tail vein injection. Half the mice were placed on drinking water with 2 mg/ml Dox (n = 5 mice/group). All mice were sacrificed at 16 days postinfection, kidneys were harvested, and fungal burdens were determined. For both species, the reduction in fungal burden in the −Dox versus +Dox groups was statistically significant (*, P < 0.01) as determined by a Mann-Whitney test. (B) The experiment in panel A was repeated using 2.1 × 105 CFU of C. tropicalis and 4.2 × 106 CFU of C. parapsilosis tetO-UME6 strains, and all mice were sacrificed at 24 h postinfection for kidney fungal burden determination. (C) The experiment in panel A was repeated for the C. parapsilosis and C. tropicalis tetO-UME6 strains using inoculum sizes of 4.5 × 106 CFU and 3.0 × 104 CFU, respectively. Mice were sacrificed at the indicated postinfection time points, and fungal burdens were determined for the indicated organs (*, P < 0.05, using a Mann-Whitney test). Please note that the fungal burden value for kidneys infected with the C. tropicalis tetO-UME6 strain in the absence of Dox at day 6 represents the lower limit of detection. (D) Examples showing the effect of UME6 expression on C. tropicalis and C. parapsilosis morphology during infection in vivo. Kidneys from mice infected with tetO-UME6 strains from the indicated species were harvested, fixed, embedded in paraffin, stained with Grocott-Gomori methenamine silver (GMS), and visualized by light microscopy (fungal cells shown in black). Black arrows indicate yeast cells. (E) The C. tropicalis WT (3.7 × 105 CFU) and nrg1Δ/Δ (3.5 × 105 CFU) strains were used to inoculate female BALB/c mice (6 to 8 weeks old) by tail vein injection (n = 5). All mice were sacrificed at 6 days postinfection, kidneys were harvested, and fungal burdens were determined. The reduction in fungal burdens in mice infected with nrg1Δ/Δ versus WT strains was statistically significant (*, P < 0.01) as determined by a Mann-Whitney test. (F) The experiment in panel E was repeated using 2.9 × 104 and 3.1 × 104 CFU of C. tropicalis WT and hgc1Δ/Δ strains, respectively. The increase in kidney fungal burden in mice infected with hgc1Δ/Δ versus WT strains was statistically significant (*, P < 0.05) as determined by a Mann-Whitney test.