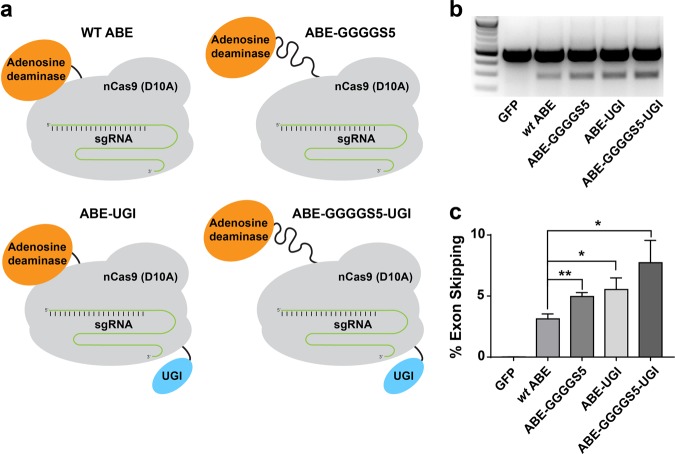
Fig. 6. Addition of both a uracil glycosylase inhibitor domain and an optimized linker further increased rates of exon skipping.
a Schematic representation of the ABE variants constructed by either modifying the linker tethering nCas9 and the deaminase domain, by fusing ABE 7.10 with a UGI or both. b Combining the GGGGS5 linker and UGI domain within the same ABE construct led to higher rates of exon skipping than the ABEs containing each modification individually, suggesting an increased A > G mutation rates in genomic DNA when both domains are used. c High-throughput sequencing analysis of RT-PCR products demonstrated significantly increased levels of exon skipping by several of the ABE variants compared with ABE 7.10. (* and ** correspond to P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 respectively by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test, n = 3)