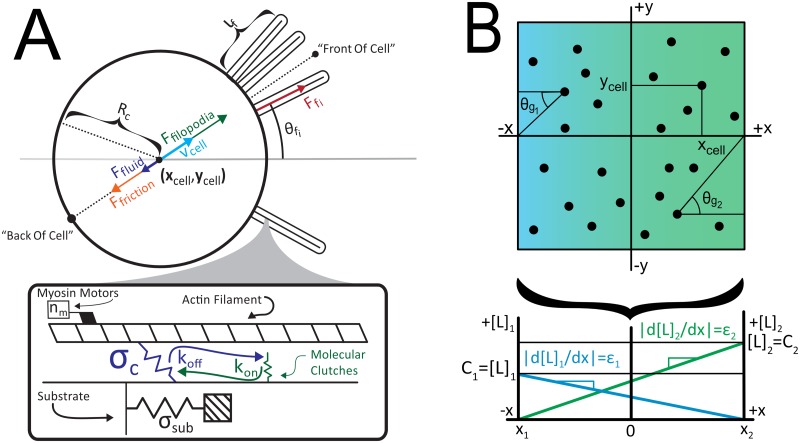
Fig 2. Schematic of the model.
A) Filopodia are modeled as a set of molecular clutches that reversibly bind to an F-actin filament undergoing retrograde flow. These clutches allow force transduction and deformation of the substrate. Each cell is modeled as a circle of radius Rc. The forces of all filopodia, Ffi, are summed to a net force Ffilopodia (green), which is balanced by resistive forces Ffriction (orange) and Ffluid (purple) to produce a velocity vcell (light blue). Also note position of the “front” and “back” of cell. B) Cells are simulated in linear, time-invariant gradients, each with a slope -εi and a maximum concentration Ci. Each gradient is oriented at an angle θgi for the ith gradient.