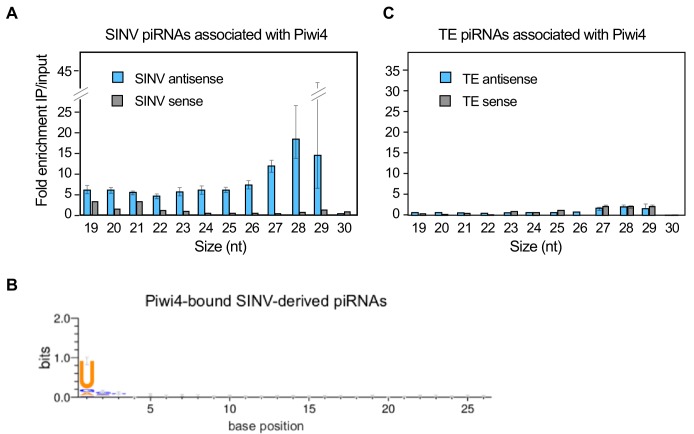
Figure 3. Piwi4 binds specifically to antisense v-piRNAs.
(A) Enrichment of SINV-derived small RNA in Piwi4-immunoprecipitation (IP) fraction compared to input sample. (B) The base bias for each position of SINV-derived piRNAs co-immunoprecipitated with Piwi4-FLAG shows a Uracil bias at position 1, characteristic of antisense Piwi-associated piRNAs (shown in bits). (C) Same as in A but for transposons (TE)-derived small RNAs.