FIGURE 1.
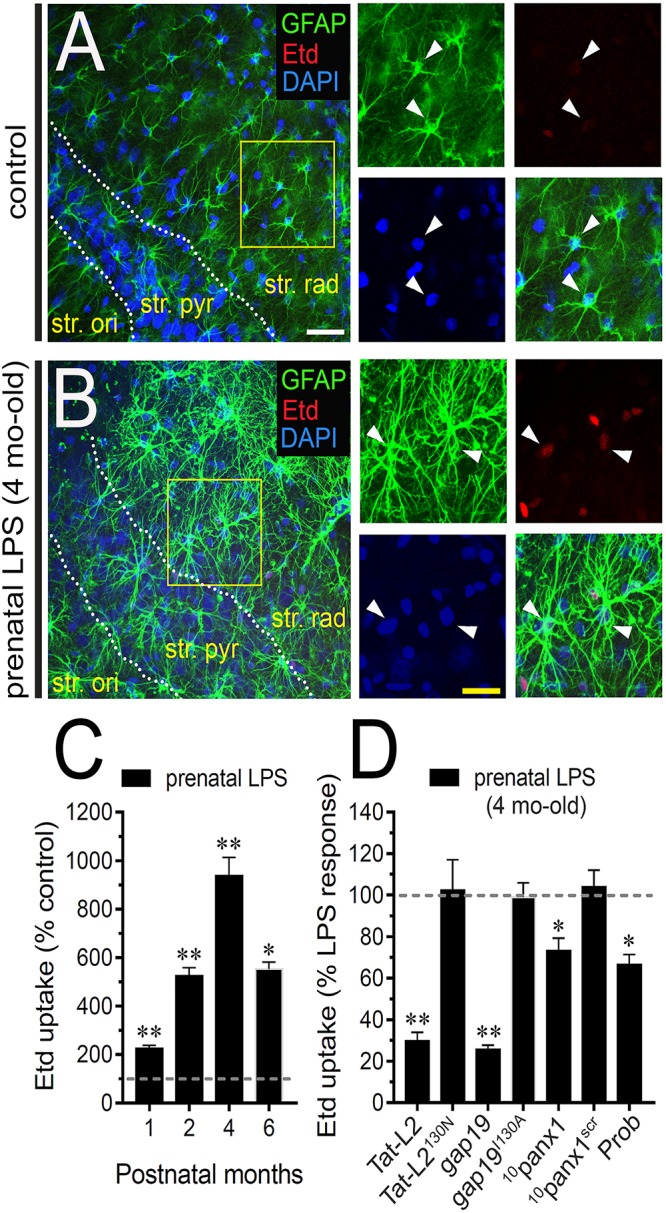
Prenatal LPS exposure augments the activity of Cx43 hemichannels and Panx1 channels by astrocytes on offspring hippocampus. Representative images showing GFAP (green), Etd (red) and DAPI (blue) staining in the hippocampus of control offspring (A) or prenatally LPS-exposed offspring (B) of 4 months old. Insets of astrocytes were taken from the area depicted within the yellow squares in (A,B). (C) Averaged data of Etd uptake normalized to control conditions (dashed line) by hippocampal astrocytes in acute slices from prenatally LPS-exposed offspring after following different postnatal periods. ∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗p < 0.001 versus control, one-way ANOVA Tukey’s post hoc test, mean ± S.E.M., n = 3. (D) Averaged data normalized to the maximal effect (dashed line) induced by prenatal LPS exposure on Etd uptake by hippocampal astrocytes in acute slices from 4 months old offspring exposed to the following pharmacological agents: 100 μM Tat-L2, 100 μM Tat-L2H126K/I130N, 100 μM gap19, 100 μM gap19I130A, 100 μM 10panx1, 100 μM 10panx1scrb and 500 μM Probenecid (Prob). ∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗p < 0.05 versus LPS, one-way ANOVA Tukey’s post hoc test, mean ± S.E.M., n = 3. Calibration bars: white bar = 180 μm; yellow bar: 100 μm.
