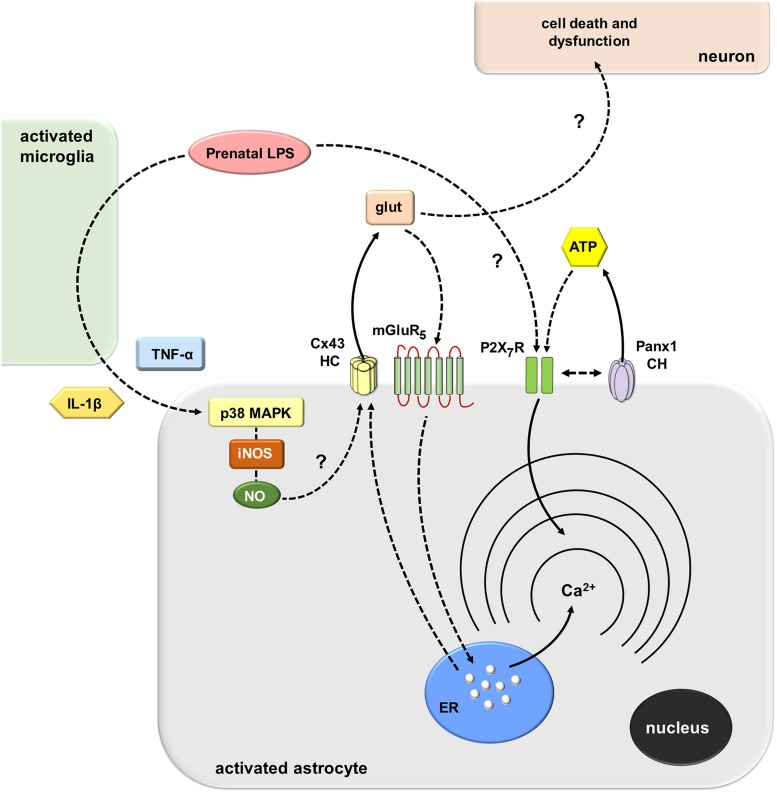
FIGURE 9.
Schematic diagram showing the possible pathways involved in the prenatal LPS-induced activation of Cx43 hemichannels/Panx1 channels and its consequences for astroglial function and neuronal survival. Prenatal LPS exposure activates microglia, resulting in the release of IL-1β and TNF-α. Both cytokines stimulate astrocytes, leading to the activation of a p38MAPK/iNOS-dependent pathway and further production of NO. The latter likely induces unknown mechanisms that cause opening of Cx43 hemichannels enabling the release of glutamate. Glutamate released via Cx43 hemichannels activates mGluR5 receptors resulting in the stimulation of IP3 receptors and further release of Ca2+ stored in the endoplasmic reticulum. In parallel, the activation of astroglial P2X7 receptors lead to the opening of Panx1 channels and further release of ATP, possibly through direct protein-to-protein interactions. Relevantly, the modulation of [Ca2+]i dynamics evoked by Cx43 hemichannels may alter astroglial morphology (not depicted), whereas the excitotoxic release of glutamate through Cx43 hemichannels may affect neuronal arborization and survival by unknown mechanisms.