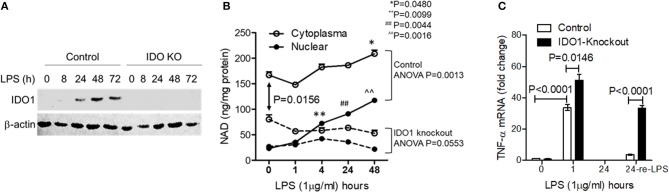
Figure 2.
Chronic inhibition of IDO1 activity minimizes cellular NAD content and prevents persistent endotoxin tolerance in response to high dose of LPS stress. IDO1 gene in THP-1 cells were gene-specifically knocked-out using CRISPR-Cas9 strategy. (A) IDO1 gene knockout precluded IDO1 protein expression in response to high dose LPS stimulation. (B) Control or IDO1 gene knockout THP-1 cells were stimulated with 1,000 ng/ml LPS for indicated times. Dynamic changes of NAD levels in cytoplasmic (the mixture of cytosol and mitochondrial NAD pools) and nuclear extracts were analyzed using colorimetric assay kits and normalized against protein contents. (C) Control or IDO1 gene knockout THP-1 cells were stimulated with 1,000 ng/ml LPS for either 1 or 24 h, and a replicate of cells at 24 h was re-stimulated with 1,000 ng/ml LPS for 1 h, TNF-α mRNA was evaluated using qRT-PCR. Data in (B,C) were shown as mean ± SD of one of three individual experiments. P-values were to show the significant changes from baseline and were calculated by post-hoc comparisons.