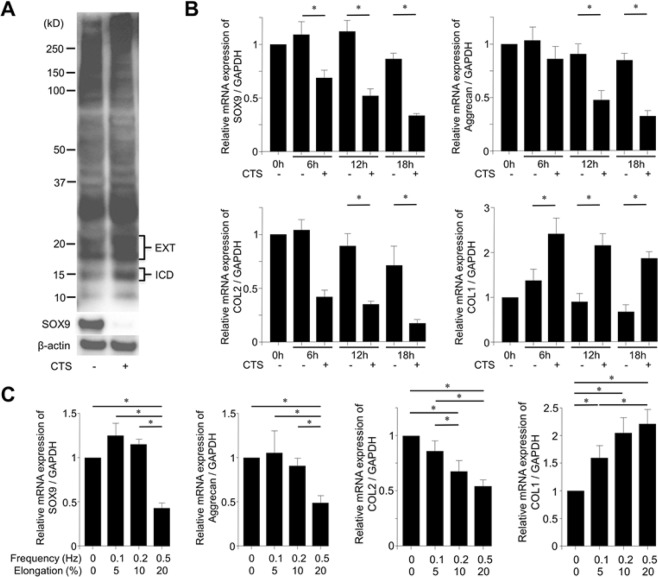
Figure 3.
Cyclic tensile strain (CTS) loading induces CD44 cleavage and de-differentiation of bovine articular chondrocytes (BACs). (A) Western blot analysis showing enhanced CD44 cleavage and decreased SOX9 expression induced by CTS loading (0.5 Hz and 20% elongation) for 12 hours. Enhanced CD44 cleavage was noted as 18–20 kD doublet C-terminal fragment (CD44-EXT) bands and the 15 kD intracellular domain (CD44-ICD) band by the polyclonal anti-CD44 antibodies. (B) Changes in articular chondrocyte-related genes by CTS loading. CTS loading significantly decreased the mRNA expression of chondrocyte differentiation markers (SOX9, aggrecan, and collagen type 2 [COL2]). In contrast, mRNA expression of a chondrocyte de-differentiation marker (collagen type 1 [COL1]) was significantly increased by CTS loading. (C) CTS loading decreased the mRNA expression of SOX9, aggrecan, and COL2 mRNA, and increased the expression of COL1 mRNA, at 12 hours. Values are mean ± standard deviation from six independent experiments. *p < 0.05.