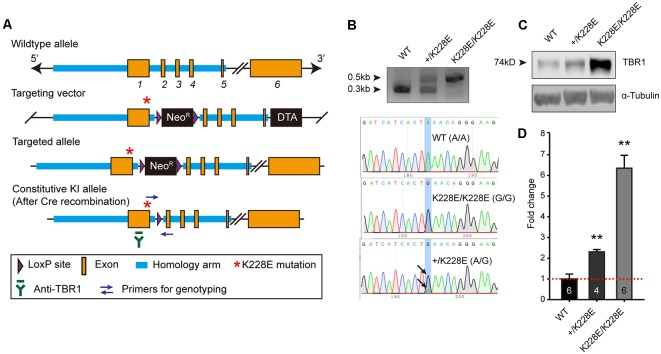
Figure 2.
Generation and basic characterization of Tbr1+/K228E and Tbr1K228E/K228E mice. (A) Tbr1 gene knock-in (KI) strategy. Note that the TBR1-K228E mutation is located in exon 1 of the Tbr1 gene. (B) PCR genotyping and confirmation of the TBR1-K228E mutation by DNA sequencing in WT, heterozygous (Tbr1+/K228E), and homozygous (Tbr1K228E/K228E) mice (E16.5). (C,D) Increased levels of TBR1 protein in Tbr1+/K228E and Tbr1K228E/K228E brains compared with that in WT brains (E17; males and females), determined by immunoblot analysis of TBR1 protein (~74 kDa) and quantification of TBR1 signals normalized to α-tubulin. The image shown is an example from male mouse samples. Note that levels of the TBR1-K228E protein are strongly increased in a gene dosage-dependent manner. n = 6 mice for WT, four mice for Tbr1+/K228E, and six mice for Tbr1K228E/K228E, **P < 0.01 vs. WT, Mann–Whitney test.