Figure 8.
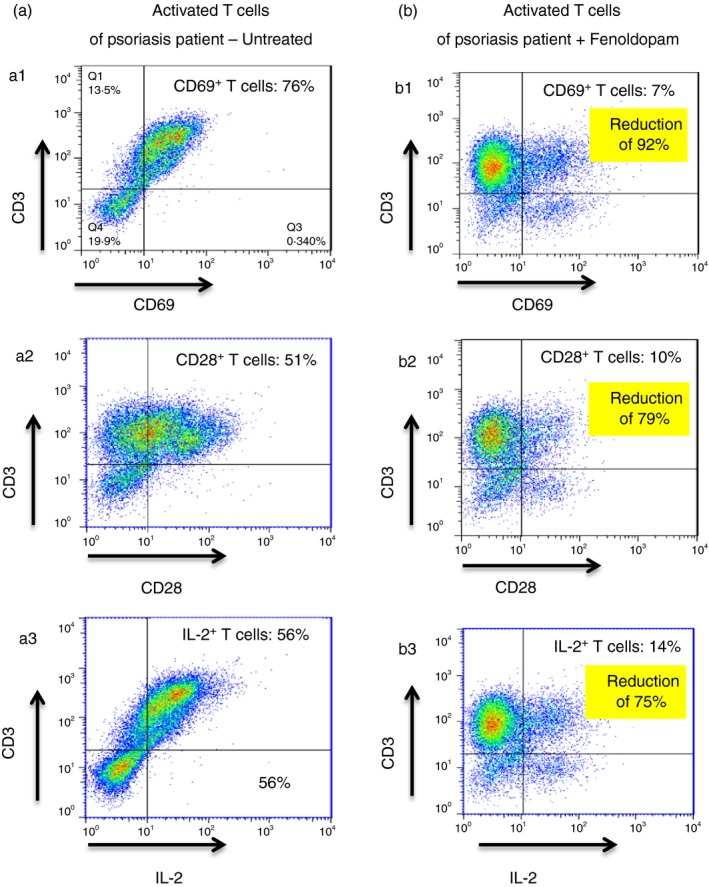
Fenoldopam induces dramatic reduction in 3 activation‐related molecules: CD69, CD28 and IL‐2, in activated T cells of Psoriasis patients. Immunostainig and flow cyometry show the following: (a1) untreated IL‐2 activated Psoriasis patient's PBMCs contain 76% of CD3+ T cells that are positive to CD69 (a2), 51% of CD3+ T cells that are positive to CD28, and (a3) 56% of CD3+ T cells that are positive to IL‐2. Following 48 hr incubation of Psoriasis patient's activated PBMCs with Fenoldopam there was a dramatic reduction in the edxdpression level of all theree T cell activation markers: (b1) Only 7% of CD3+ T cells are positive to CD69, (b2) only 10% of CD3+ T cells are positive to CD28, and (b3) only 14% of CD3+ T cells are positive to IL‐2. For all the flow cytometric analysis plots, isotype‐matched control antibodies were used to determine non‐specific staining. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 5). Statistical analysis was performed using the Kruskal–Wallis test. Statistical significance was set at P < 0·05.
