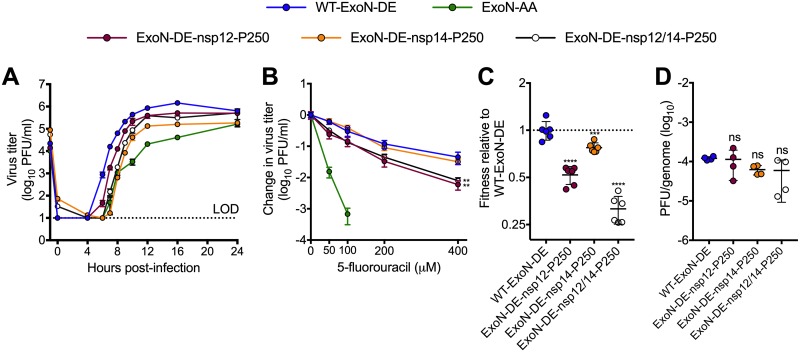
FIG 4.
Mutations that increase ExoN-AA fitness are detrimental in the presence of WT-ExoN-DE. (A) Replication kinetics of indicated viruses at an MOI of 0.01 PFU/cell plotted as means ± standard deviations (n = 3). (B) 5-Fluorouracil sensitivity at an MOI of 0.01 PFU/cell (means ± standard deviations of n = 6). (C) Competitive fitness of individual recombinants relative to WT-ExoN-DE. Viruses were competed with a tagged WT-ExoN-DE reference strain, and relative fitness was normalized to the mean value of the WT-ExoN-DE (means ± standard deviations of n = 6). (D) Specific infectivity (genomes per PFU) from isolated infections (means ± standard deviations of n = 4). Statistical significance of each virus relative to that of WT-ExoN-DE was determined with two-way analysis of variance with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test (B) or by ordinary one-way analysis of variance with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test (C and D). **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant. LOD, limit of detection.