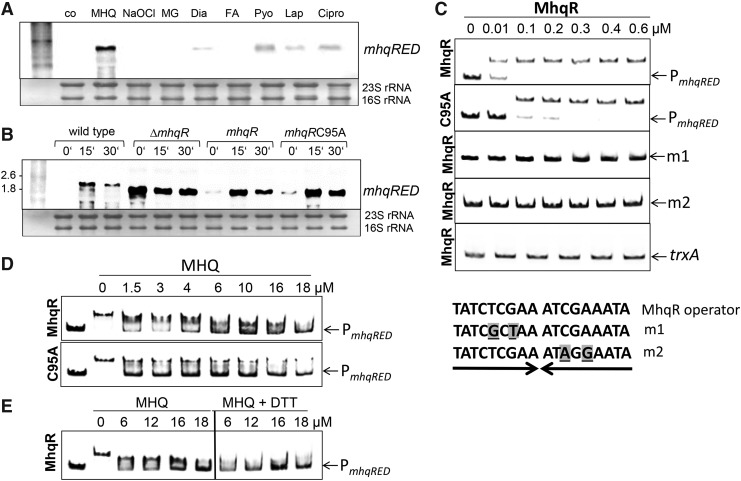
FIG. 4.
Transcriptional induction of the MhqR regulon under quinones, aldehydes, and antimicrobials and the quinone response of MhqR in DNA binding assays in vitro. (A) Transcription of the mhqRED operon was analyzed using the Northern blots in S. aureus COL wild type 30 min after exposure to 45 μM MHQ, 1 mM NaOCl, 0.5 mM methylglyoxal (MG), 2 mM diamide (Dia), 0.75 mM formaldehyde (FA), 300 μM lapachol (Lap), 90.5 μM ciprofloxacin (Cipro), and 76 μM pyocyanin (Pyo). The compounds were added at an OD500 of 0.5. The mhqRED operon responds most strongly to MHQ and less strongly to lapachol, pyocyanin, and ciprofloxacin. (B) The Northern blot analysis was performed with RNA of the wild type, the mhqR mutant, and the mhqR and mhqRC95A complemented strains before (0 min) and 15 and 30 min after MHQ stress. Cys95 is not required for DNA binding and quinone sensing of MhqR in vivo. The methylene blue stain is the RNA loading control indicating the 16S and 23S rRNAs. (C) MhqR binds specifically to the mhqRED promoter in vitro. EMSAs were used to analyze the DNA binding activity of increasing amounts (0.01–0.6 μM) of MhqR and MhqRC95A proteins to the mhqRED promoter (PmhqRED) in vitro. To test the specificity of binding, two base substitutions were introduced in each half of the inverted repeat, denoted in gray and underlined (m1 and m2). As nonspecific control DNA probe we used the trxA gene. The arrows denote the free DNA probe and the shifted band indicates the DNA-MhqR promoter complex. (D) EMSAs of MhqR and MhqRC95A proteins (0.6 μM) to the mhqRED promoter were performed to study the inactivation of MhqR by increasing amounts of MHQ (1.5–18 μM) leading to the loss of DNA binding. The arrows denote the free mhqRED promoter probe and the shifted band indicates the DNA-MhqR promoter complex. (E) MhqR inactivation by quinones could not be reversed with 1 mM DTT, which was added to the MhqR-DNA binding reaction 30 min after MHQ addition. Cys95 is not important for MHQ sensing or DNA binding of MhqR in vitro. DTT, dithiothreitol; EMSA, electrophoretic mobility shift assay; NaOCl, sodium hypochlorite.