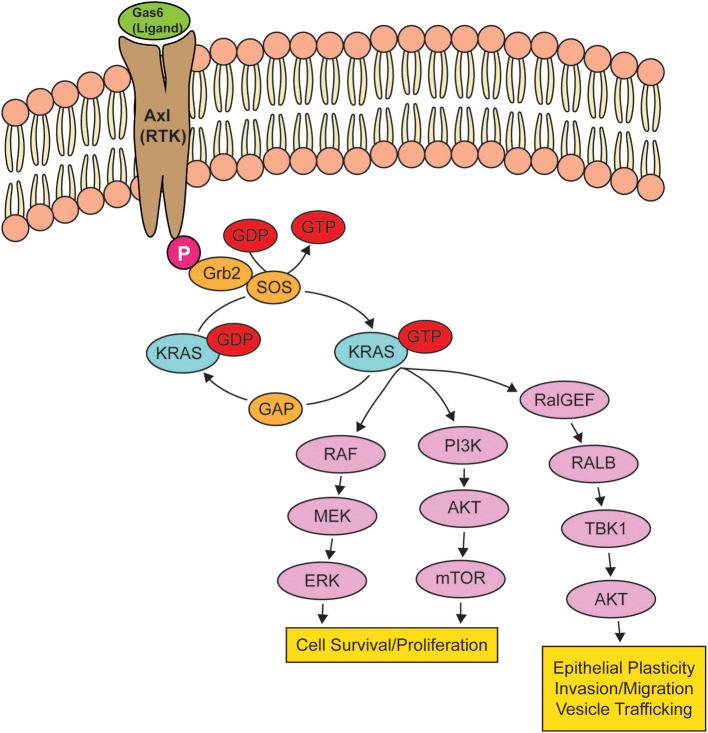
Figure 2.
Oncogenic KRAS effector pathways. When a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) is activated by its ligand, KRAS binds to GTP, rendering it active until the GTP hydrolyzes to GDP, turning KRAS off. When KRAS is mutated, KRAS remains bound to GTP, leading to the overstimulation of KRAS signaling pathways, resulting in cell survival and proliferation, epithelial plasticity, and migration. The activation of RTK AXL by GAS6 is shown as a potential signaling pathway that can drive an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the activation of KRAS.