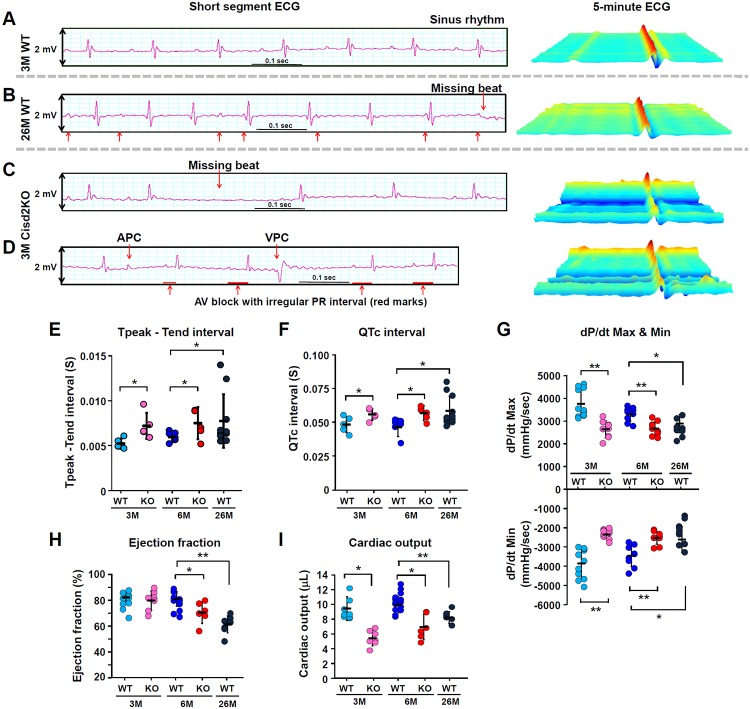
Fig 2. Cisd2KO mice exhibit cardiac electromechanical dysfunctions that are similar to those observed in the naturally aged WT mice.
(A-D) Representative ECG tracings and continuous 5-minute waterfall plots recorded following anesthesia of the mice. A normal sinus rhythm ECG recorded from a young (3M) WT mouse (A). The irregular PR interval and missing beats recorded from an aged (26M) WT mouse (B). Representative dysrhythmic ECGs, namely a missing beat (C), AV block with irregular and progressive prolongation of PR interval, APCs, and VPCs (D), which were found in the Cisd2KO mice at 3M. (E and F) Measurements of the Tpeak–Tend intervals (E) and the QTc intervals (F) were obtained from 5 minutes of sequential beats obtained from whole ECG tracings. (G) Peak developed pressures and rates of pressure increase and rates of pressure decrease during left ventricular contraction; these were measured by Millar’s catheter in the mice. The dP/dt max is the maximal rate of pressure development, and the dP/dt min is the maximal rate of decay of pressure. The WT mice exhibited an age-dependent progression with respect to cardiac dysfunction with a reduced dP/dt Max and dP/dt min. (H and I) Left ventricular ejection fraction (H) and cardiac output (I) were measured and quantified by cardiac MRI. Data are presented as mean ± SD and are analyzed by Student t test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005. Mouse number n ≥ 5 for each group. Values for each data point can be found in S1 Data. 3M, 3 months old; 6M, 6 months old; 26M, 26 months old; APC, atrial premature complex; AV, atrioventricular; Cisd2KO, CDGSH iron-sulfur domain-containing protein 2 KO; ECG, electrocardiography; KO, knockout; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; QTc, corrected QT; VPC, ventricular premature complex; WT, wild type.