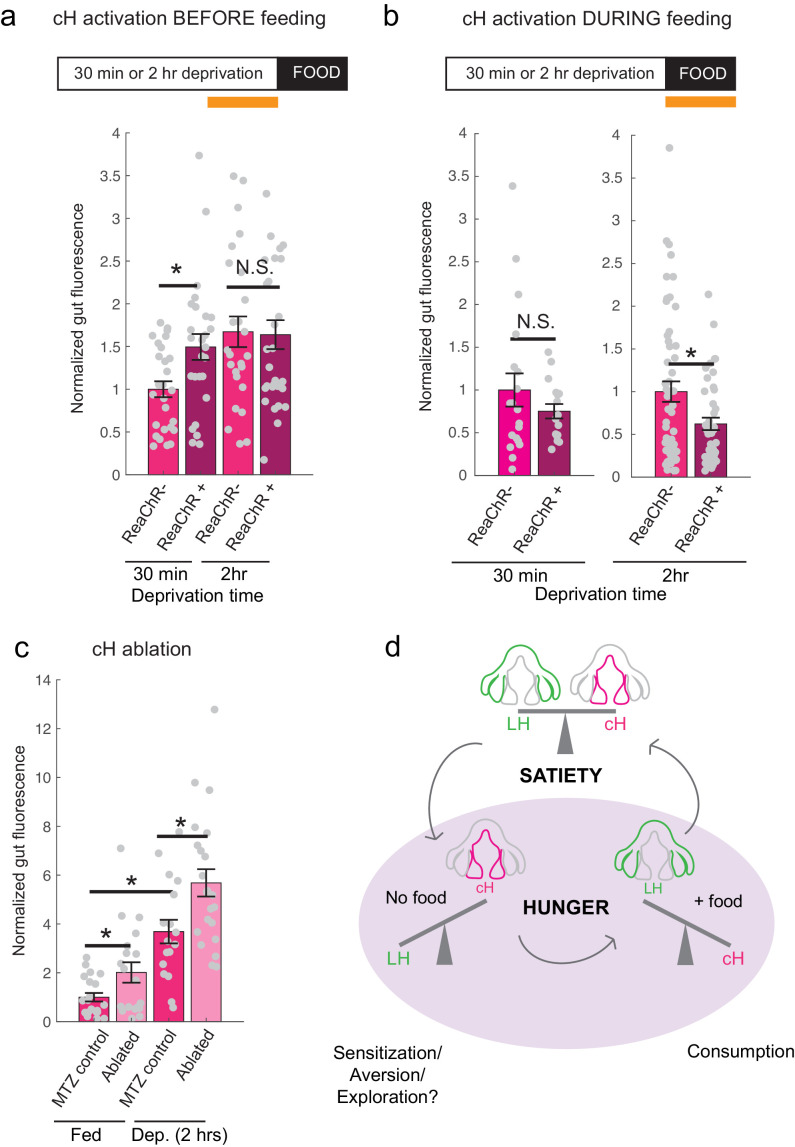
Figure 6. Role of the cH in behavioral control.
(a) Animals expressing the ReaChR transgene Tg(UAS:ReaChR-RFP) under control of the Tg(y333:Gal4) driver were exposed to 630 nm illumination (orange bar in schematic) for 10 min prior to feeding and assessed for subsequent ingestion of fluorescently labeled paramecia. Tg(y333:Gal4; UAS:ReaChR-RFP) stimulation increased food intake in 30 min food-deprived but not 2 hr food-deprived fish, during subsequent food presentation. Dep. (30 min): n = 27/26 (ReaChR-/ReaChR+), p = 0.005. Dep. (2 hr): n = 25/29 (ReaChR-/ReaChR+), p = 0.36, one-tailed Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Asterisks denote p<0.05. Since ReaChR expression via Tg(116A:Gal4) was negligible, we used another Gal4 (Tg(y333:Gal4)) line that is also specific to the cH when ReaChR is expressed. Fed and food-deprived fish were assayed simultaneously, thus all results were normalized to fed controls. ReaChR- controls do not have visible Tg(y333:Gal4;UAS:ReaChR-RFP) expression, and thus are a mixture of siblings expressing Tg(y333:Gal4) only, Tg(UAS:ReaChR-RFP) or neither of these transgenes, each with ⅓ probability. (b) Left: Optogenetic activation of Tg(y333:Gal4; UAS:ReaChR-RFP) fish (orange bar in schematic) during feeding in fish that were food-deprived for 30 min does not significantly reduce food intake: n = 19/16 (ReaChR-/ReaChR+), p = 0.44 (N.S.); Right: Optogenetic activation of Tg(y333:Gal4; UAS:ReaChR-RFP) fish during feeding in 2 hr food-deprived fish reduces food intake: n = 53/44 (ReaChR-/ReaChR+), p = 0.042. Since 30 min and 2 hr food-deprived fish were assayed in different experiments, gut fluorescence normalized to their respective controls, one-tailed Wilcoxon rank-sum test. (c) Nitroreductase-mediated ablation of the cH in Tg(116A:Gal4;UAS:nfsb-mCherry)-positive or negative fish treated with metronidazole (MTZ) from 5 to 7 dpf significantly enhances food intake in 8 dpf fish. p = 0.0042/0.041/1.4 × 10−5 (fed control vs fed ablated, 2 hr dep. control vs 2 hr dep. ablated, fed vs 2 hr dep.), n = 29 (fed control)/28 (fed ablated)/22 (dep. control)/29 (dep. ablated), two-tailed Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Controls do not have visible Tg(116A:Gal4;UAS:nfsb-mCherry) expression, and thus are a mixture of siblings expressing Tg(116A:Gal4) only, Tg(UAS:nfsb-mCherry) or neither of these transgenes, each with ⅓ probability. (d) Schematic summarizing our results. We propose distinct roles of the cH during hunger, depending on the presence or absence of food. See Appendix 1 – Conceptual Circuit Model for elaboration. Data plotted in Figure 6 are provided in Figure 6—source data 1.