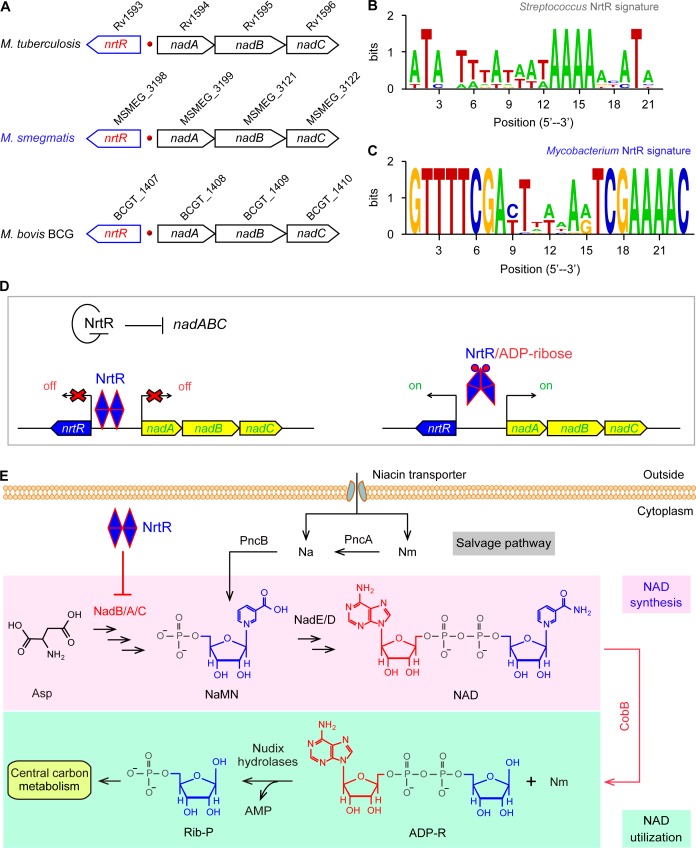
Figure 1. Working model for the regulation of NAD homeostasis by NrtR in Mycobacterium.
(A) The genetic context of nrtR and its signature in Mycobacterium compared with the NrtR-binding sequences in Streptococcus (B) and Mycobacterium (C). (D) NrtR acts as an auto-repressor and represses the transcription of the nadA-nadB-nadC operon that is responsible for the de novo synthesis of the NAD+ cofactor in Mycobacterium. (E) NAD+ homeostasis proceeds through cooperation of a salvage pathway with de novo synthesis in Mycobacterium. Designations: nadA, the gene encoding quinolinate synthase; nadB, gene encoding L-aspartate oxidase; nadC, gene encoding quinolinate phosphoribosyltransferase; PncA, nicotinamide deaminase; PncB, nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase; NrtR, a bifunctional transcriptional factor involved in the regulation of NAD+ synthesis; ADP-R, ADP-ribose; Na, nicotinic acid; Nm, nicotinamide; Rib-P, ribose-5-phosphate; Asp, aspartate; NaMN, nicotinate mononucleotide; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; CobB, an NAD+-consuming deacetylase.