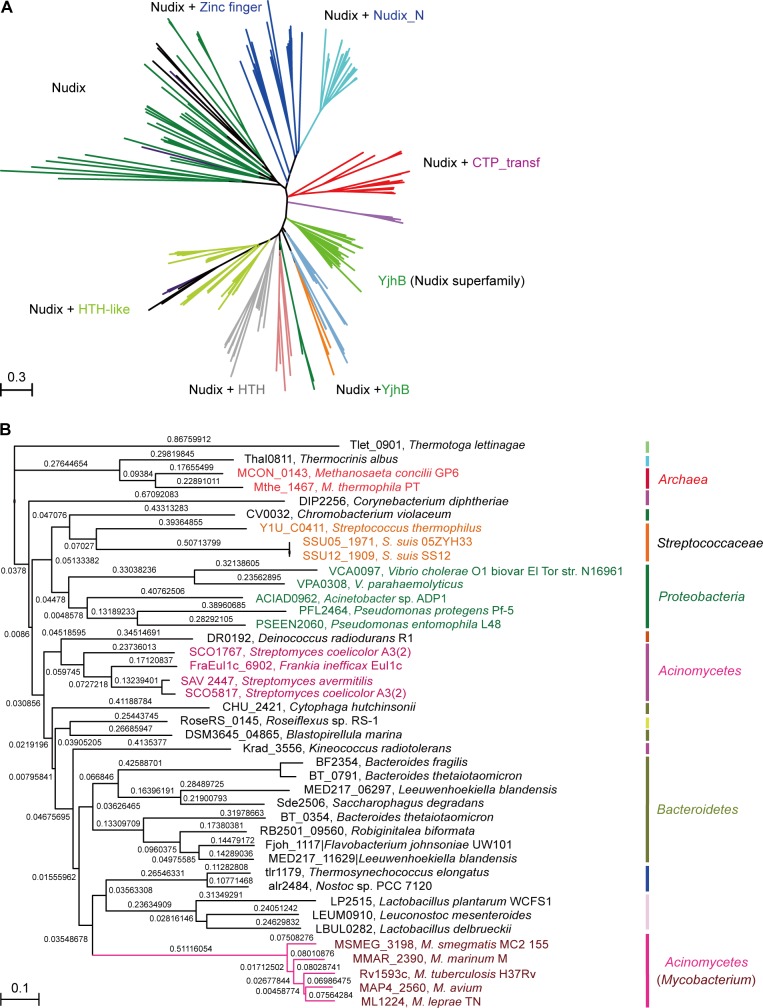
Figure 2. Phylogeny of NrtR proteins.
(A) The unrooted radial phylogeny of Nudix-like proteins. A variety of distinct subclades involve homologs containing a Nudix domain alone, a Nudix domain combined with DNA-binding domains or zinc finger domains, a Nudix domain combined with a CTP-transf (Cytidylyltransferase family) domain, Nudix+Nudix_N (Nudix located at N-terminal), or a Nudix pyrophosphate hydrolase with ADP-ribose substrate preference (YjhB, Nudix+YjhB superfamily). These distinct subclades seem to coincide with known taxonomic groups with few exceptions. NrtR candidates in Mycobacterium, Vibrio and Streptococcus species are indicated with purple, green and orange text, respectively. (B) Hierarchical tree of NrtR homologs. Several distinct sub-clades are clustered in a pattern that is generally consistent with bacterial taxonomic groups. The protein-sequence-based phylogeny of NrtR homologs was inferred using the maximum likelihood method and the WAG substitution model. The evolutionary distance for each node is shown next to the branches. Gene locus tags and strain names corresponding to the protein sequences used are indicated in the figure.