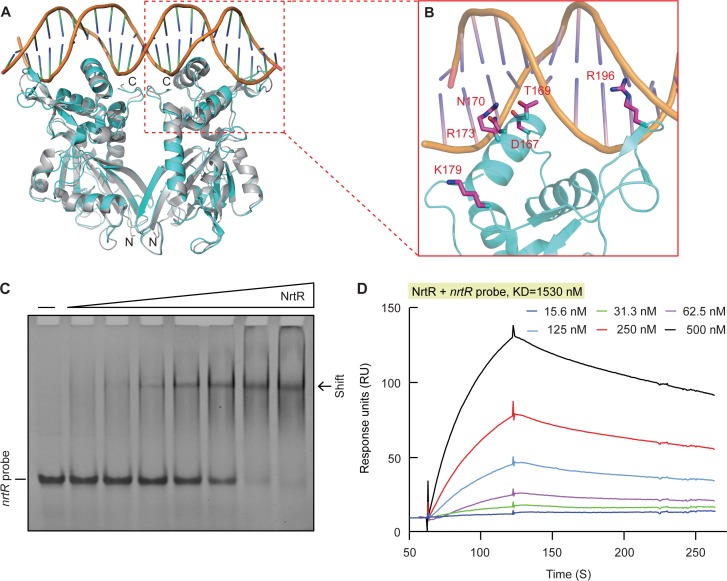
Figure 3. Structural and functional insights into the binding of MsNrtR to its cognate DNA target.
(A) Structural analysis of the predicted DNA-binding motif through structural modeling of M. smegmatis NrtR (http://swissmodel.espasy.org/). The image shows the superposition of M. smegmatis NrtR with the Shewanella oneidensis NrtR-DNA complex (PDB: 3GZ6). MsNrtR is highlighted in cyan and soNrtR is indicated in gray. Double-stranded DNA is denoted by two orange lines. (B) Structural prediction of the critical DNA-binding residues of the M. smegmatis NrtR. The six residues (D167, T169, N170, R173, K179, and R196) that are implicated in direct or indirect contact with cognate DNA are labeled in red. (C) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA)-based visualization of the interaction of MsNrtR with the nrtR probe. The amount of NrtR protein incubated with the DNA probe is in each lane is (left to right): 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, and 40 pmol. (D) Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) measurements of M. smegmatis NrtR binding to the nrtR promoter. NrtR protein at various concentrations (typically 15.625–500 nM) were injected over the immobilized DNA probe comprising of the NrtR palindrome of nrtR gene. KD, kd/ka, ka, association constant; kd, dissociation constant; RU, response units.
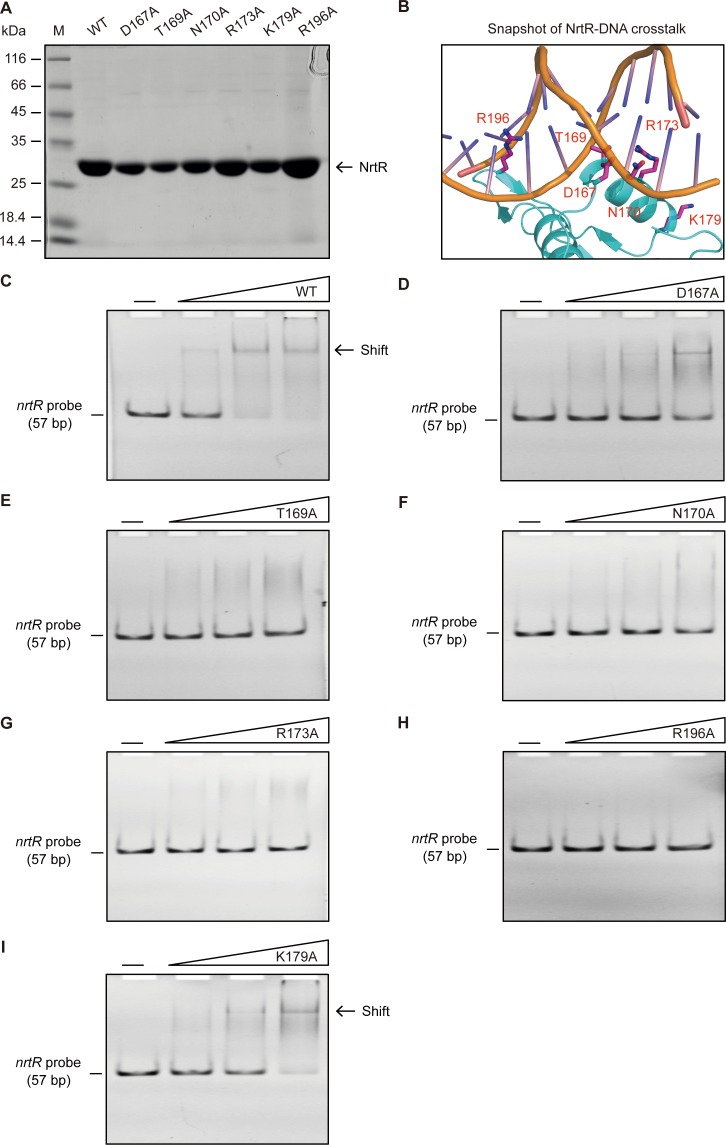
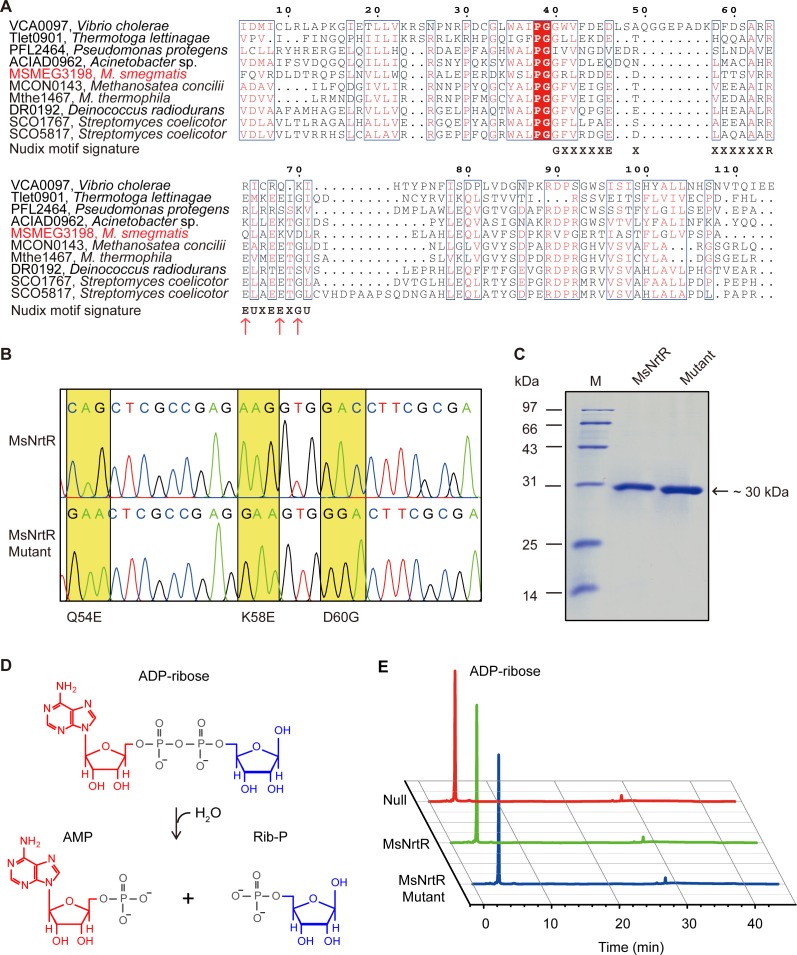
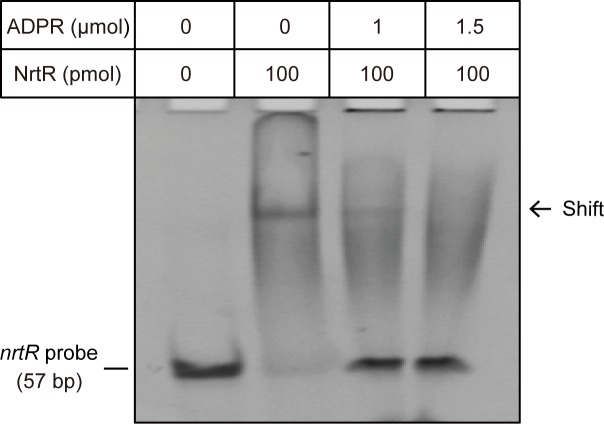
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Characterization of the M. smegmatis NrtR.
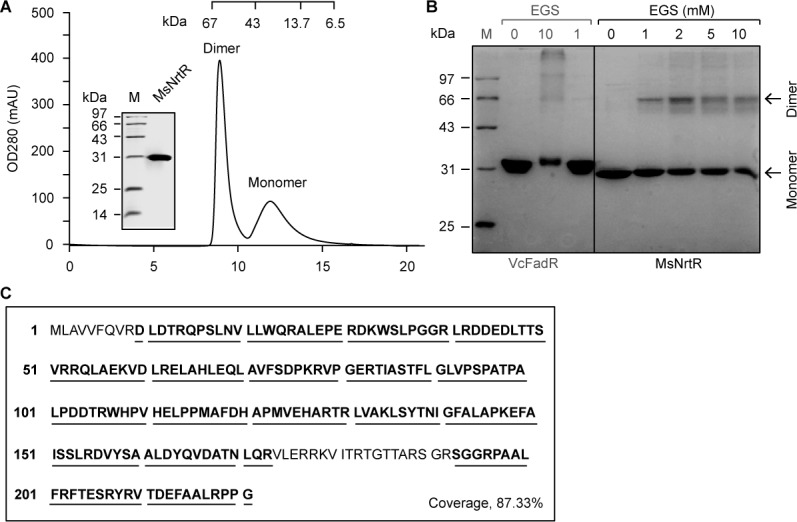
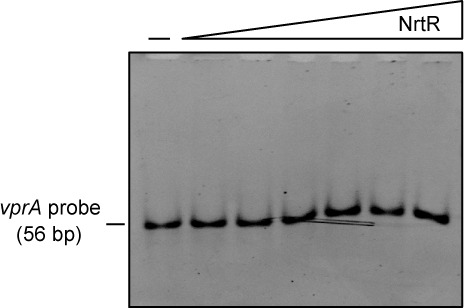
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. The M. smegmatis NrtR cannot bind to an unrelated DNA, the vprA probe.