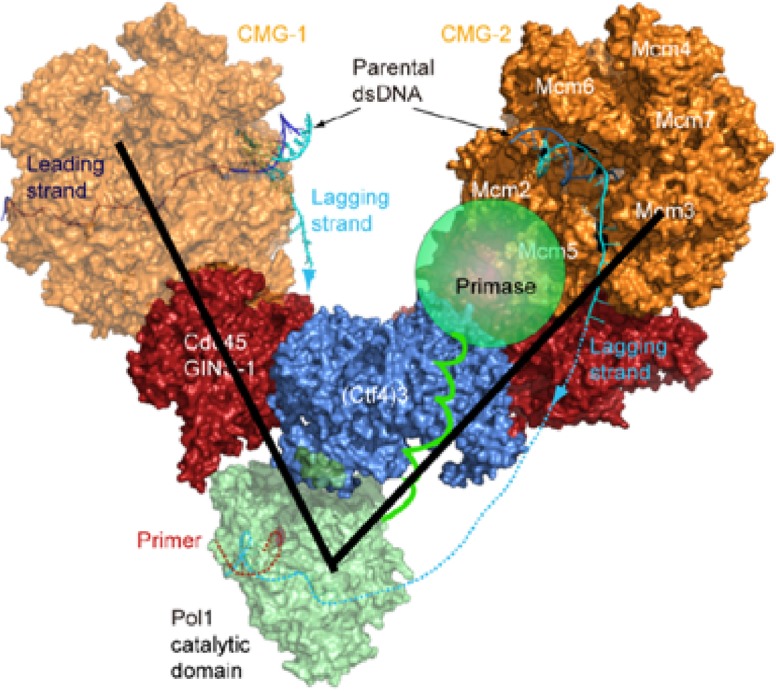
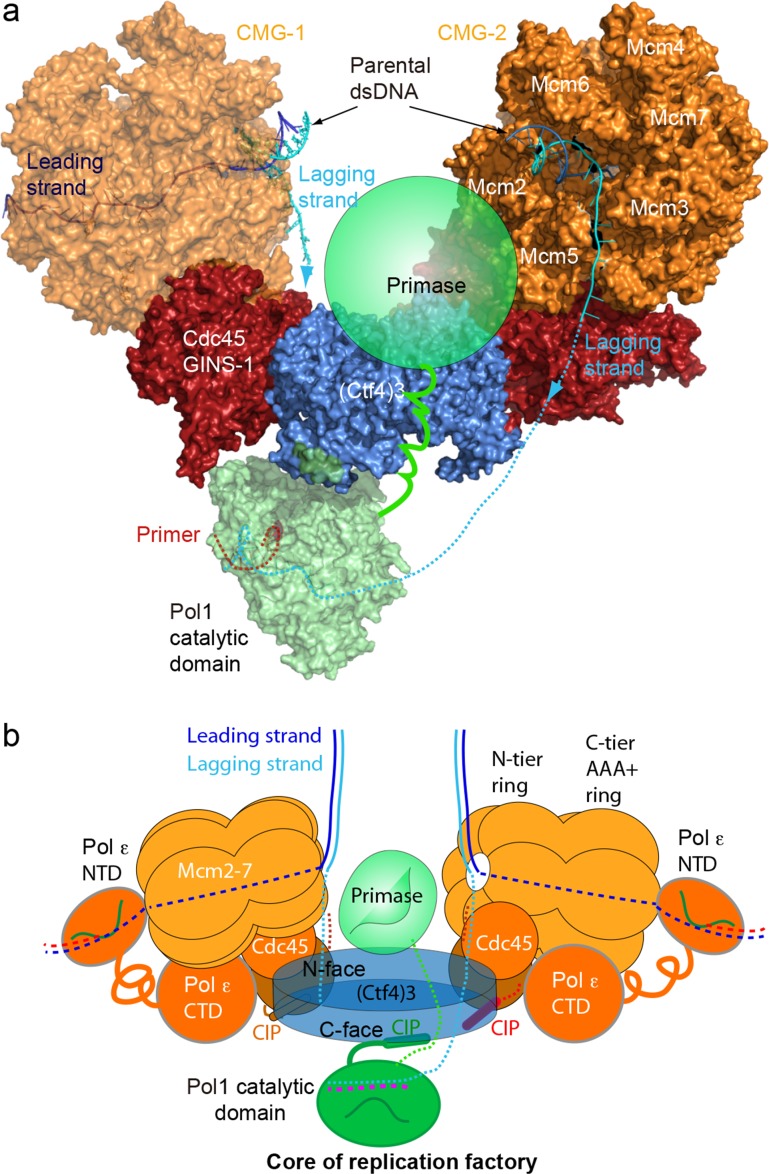
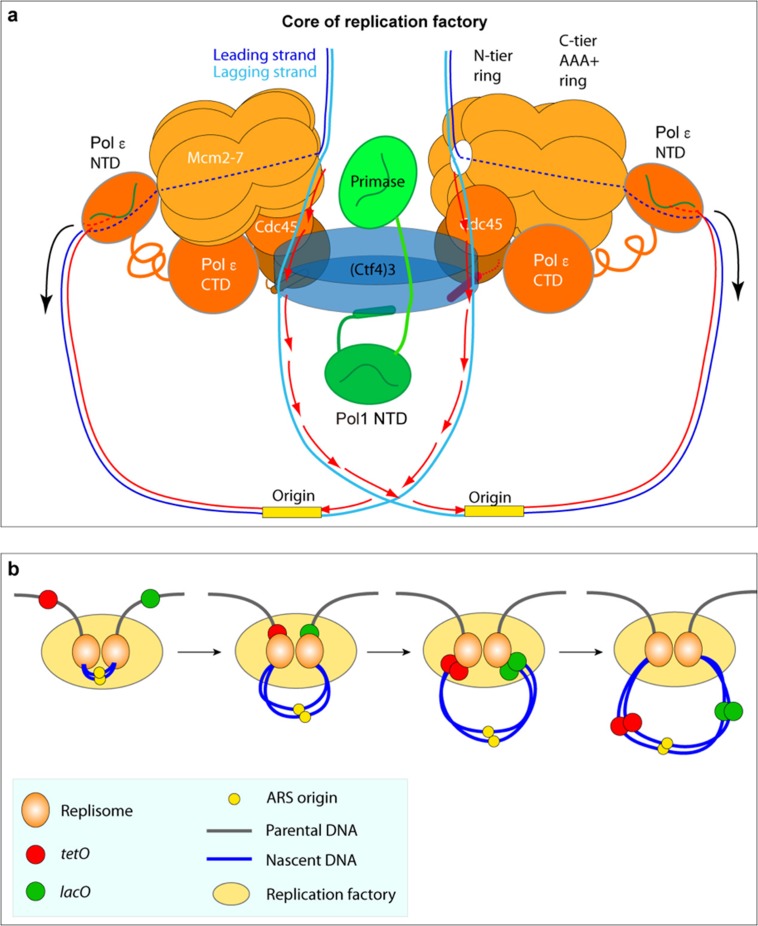
Figure 8. A model for the coupled sister replisomes.
(a) A composite atomic model of one Pol α-primase and two CMG helicases organized in a core factory with a Ctf4 trimer. The model is derived by aligning Ctf43 shared between the Ctf43–CMG dimer model and the model of Ctf43–Pol α NTD. The DNA structure is based on the structure of CMG–forked DNA (PDB 5U8S), but the lagging strand outside the CMG channel is modeled. The possible location of the primase module of Pol α-primase is indicated by a green ellipse. (b) A sketch illustrating the leading strand Pol ε at the C-tier face of the CMG helicase and the primase reaches atop the N-face of Ctf43, potentially capable of priming both lagging strands. See text for details. See also Figure 8—figure supplements 1 and 2, and Video 3. Figure Supplements and their legends.
Figure 8—figure supplement 1. The Pol1 and primase lobes of Pol α-primase have a 70° range of motion.