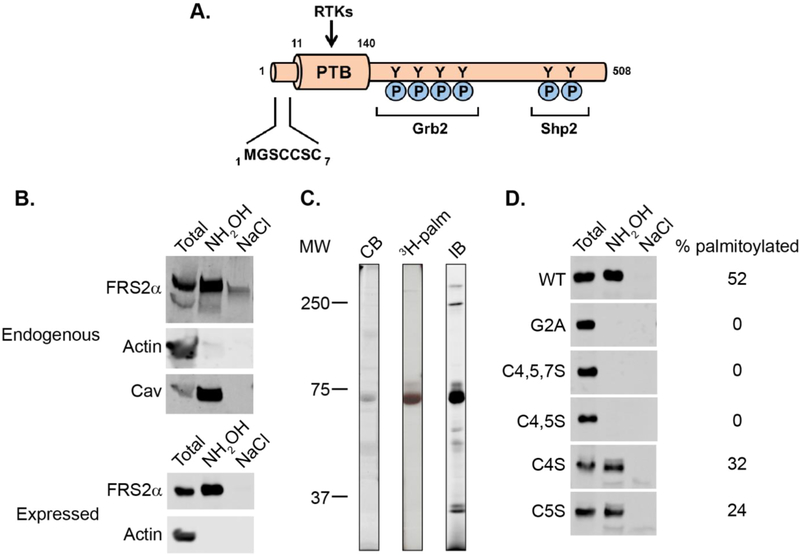
Figure 1.
Palmitolylation of FRS2α. (A) Scheme of human FRS2α showing the N-terminal lipidation motif, RTK-binding PTB domain, and phosphotyrosines that interact with Grb2 and Shp2. (B) Palmitoylation of endogenous FRS2α in HEK293 cells (top) and overexpressed FRS2α-DDK in HeLa cells (bottom) detected by acyl-RAC (see Supporting Information). Actin and caveolin are negative and positive controls, respectively. Total represents 10% of the sample used for analysis. (C) 3H-palmitate incorporation into overexpressed FRS2α-DDK immunoprecipitated with anti-DDK antibodies from 3H-palmitate-labeled HeLa cells. Abbreviations: CB, Coomassie blue-stained gel; 3H-palm, autoradiogram; IB, immunoblot with anti-DDK antibody. (D) Palmitoylation of DDK-tagged FRS2α (WT and mutants) expressed in HeLa cells as detected by acyl-RAC. Total represents 10% of the sample used for analysis.