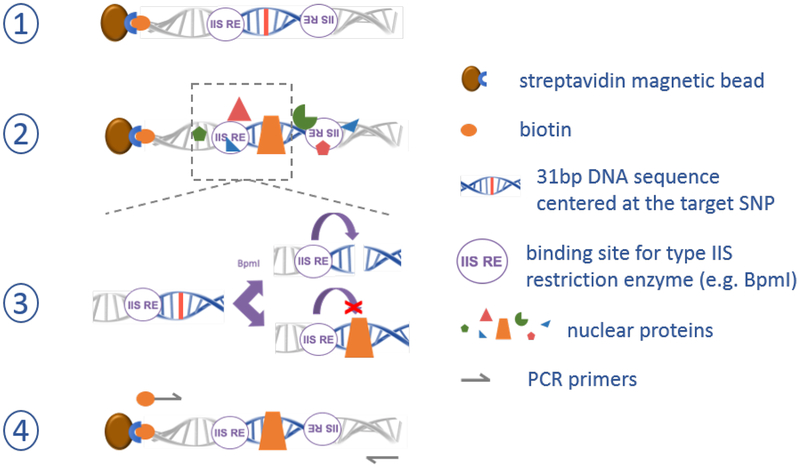
Figure 2. SNP-seq methodology to screen non-coding DNA variants for regulatory protein binding.
Step 1) a library of synthetic DNA constructs is generated containing each allele of each candidate non-coding variant near a GWAS tagging SNP within its local 31bp context. Step 2) the library of constructs is exposed to nuclear extract from candidate cells, and non-binding proteins are washed away. Step 3) constructs are incubated with a type IIS restriction factor (here BpmI); constructs in which a protein binds the candidate SNP are shielded from cleavage. Step 4) PCR using one biotinylated and one non-biotinylated PCR primer are used to regenerate the library for another round of screening, typically repeated 5–10 times to enable sufficient amplification, followed by next-generation sequencing to identify surviving sequences as candidate fSNPs.