Figure 3.
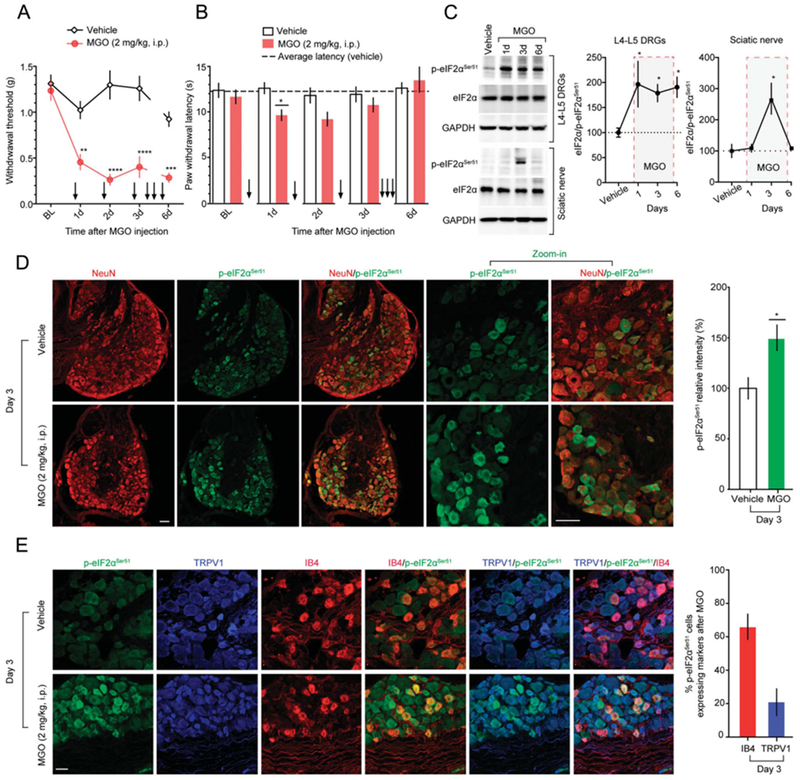
Methylglyoxal produces pain hypersensitivity and triggers the ISR in DRG neurons in vivo. (A) Daily administration of MGO (2 mg/kg, i.p; for 6 days) markedly increases mechanical sensitivity in mice tested at 3 hours after MGO injection. Two-way ANOVA, F(4, 40) = 7.156, P = 0.0002. Post-hoc Bonferroni; vehicle vs MGO at 1 days: **P = 0.0012, at 2 days: ****P < 0.0001, at 3 days: ****P = 0.0001, and at 6 days: ***P = 0.002. n = 6. (B) Methylglyoxal (2 mg/kg, i.p) produces a transient thermal hypersensitivity. Two-way ANOVA, F(4,107) = 1.771, P = 0.1400. Post-hoc Bonferroni; vehicle vs MGO at 1 day: *P = 0.0329. n = 12. (C) Methylglyoxal (2 mg/kg, i.p) produces a sustained increase on eIF2αSer51 phosphorylation, from day 1 to 6, in L4-L5 DRGs. One-way ANOVA, F(3,9) = 3.742, P = 0.05; post-hoc Dunnett: veh vs MGO at 1 day: *P = 0.0479, at 3 days: *P = 0.0456, at 6 days: *P = 0.0259. n = 4. Methylglyoxal also produces a transient significant increase on p-eIF2αSer51 at day 3 in the sciatic nerve of mice. One-way ANOVA, F(3,11) = 7.35, P = 0.0056. Post-hoc Dunnett: *P = 0.0055, vehicle vs MGO at day 3. n = 4. (D) The increase on eIF2αSer51 phosphorylation in the DRGs at day 3 is mainly present in neurons as shown by the colocalization with the neuronal marker NeuN. Unpaired t test: t = 2.967; *P = 0.0048, vehicle vs MGO. n = 24. (E) After i.p. MGO administration, 65.96% of p-eIF2α-positive cells in the DRG express IB4 and 20.82% express TRPV1. Scale bar, 50 μm. ANOVA, analysis of variance; ISR, integrated stress response.
