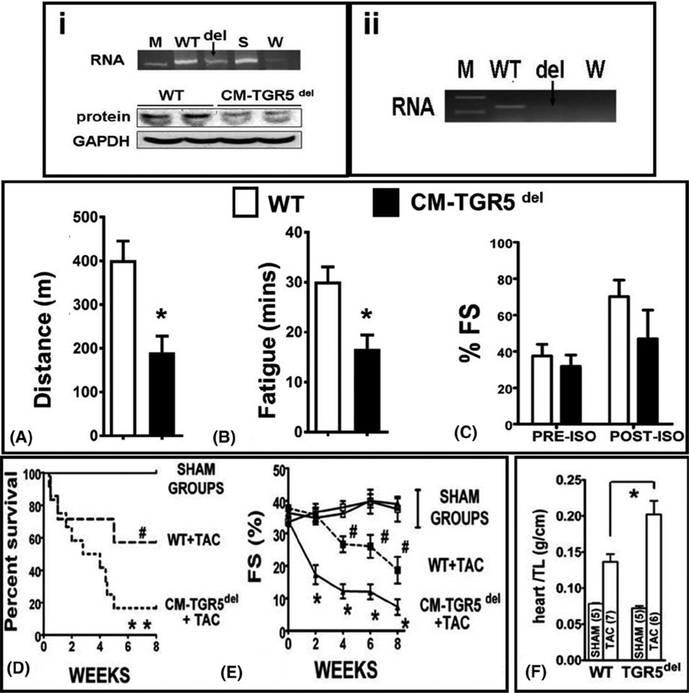
FIGURE 5.
Cardiomyocyte specific deletion of TGR5 (CM-TGR5del) in mice, demonstrate exercise intolerance, increased mortality and exaggerated contractile dysfunction in response to TAC, compared to littermates: (i) and (ii) shows proof of TGR5 deletion from the whole heart and adult isolated cardiomyocyte in CM-TGR5del mice. (i) shows knockdown of TGR5 from the whole hearts in CM-TGR5del mice at both RNA and protein level using primers and antibodies used and tested by us before. As this is a cardiomyocyte specific deletion, weak bands seen on PCR and Western blots are a result of presence of TGR5 in the vascular endothelium which is not deleted. A ~60% deletion was achieved from the whole heart when quantified objectively by qRTPCR and densitometry (data not shown). [M] is marker, [WT] is whole hearts of TGR5 flox/flox/cre− littermates, deletion (del) shown as arrow [CM-TGR5del hearts], with spleen(S) as positive control and water (W) as negative control. (ii) shows complete deletion of TGR5 from adult cardiomyocytes. We isolated cardiomyocytes from the hearts of adult CM-TGR5del mice and probed them for the presence of TGR5 using primers as before. We found a near complete deletion of TGR5 RNA (arrow). [WT] is whole hearts of TGR5 flox/flox/cre− mice, deletion (del) shown as arrow [CM-TGR5del hearts], water [W] as negative control. When challenged with acute physiologic stress in the form of treadmill exercise, CM- TGR5del mice ran shorter distance (A) and fatigued (B) earlier than WT mice. (n = 5/group; Statistics: t test; *P < 0.05; RESULTS: Mean ± SEM). There was no significance in shortening fraction between the two groups on isoprenaline (C). When CM-TGR5del mice were randomized to SHAM or TAC, increased mortality was noted in CM-TGR5del mice compared to WT mice post-TAC (D). No mortality noted in sham groups. (*P = 0.013 compared to all groups; # P < 0.05 compared to sham (Stats: Mantell-Cox test, n = 3/grp in SHAM and 10/grp in TAC). (E) shows serial analysis of shortening fractions (%FS) as evaluated by ECHOs. Note significant decrease in FS in CM- TGR5del mice post- TAC over 8 wk, starting as early as 2 wk (n = 3–5/grp; Stats: Multiple comparison ANOVA, P < 0.05). (F) shows bar graphs of heart weight/tibial length ratios of WT and CM-TGR5del mice who undergo either SHAM or TAC. CM- TGR5del mice had ~60% higher heart weight/TL ratio suggesting increased hypertrophy compared to WT+TAC mice. (*P < 0.05; ANOVA; Results: Mean ± SD; number of animals = WT + SHAM (n = 3); WT+TAC (n = 7 survived of 10); CM- TGR5del + SHAM (n = 3); CM- TGR5del (n = 6 survived of 20)