Fig. 1.
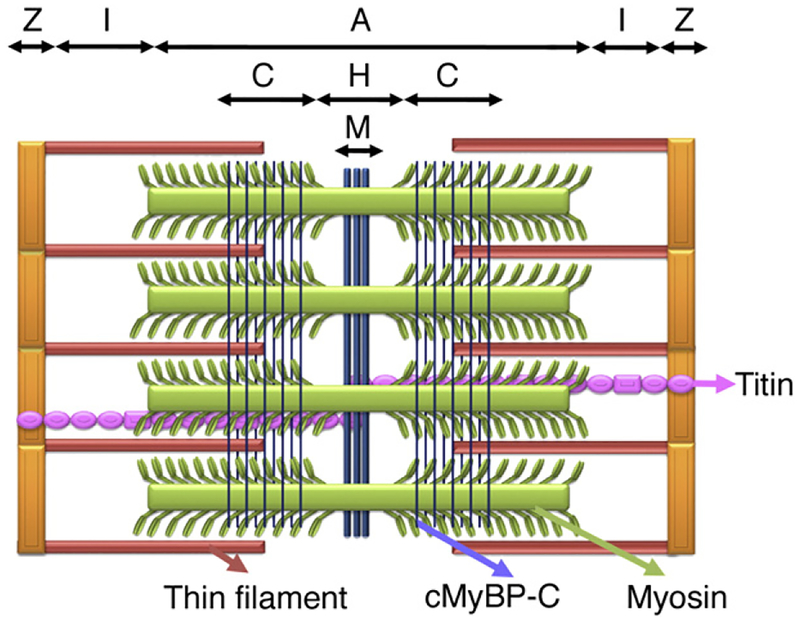
Schematic diagram of the cardiac sarcomere and arrangement of cMyBP-C. The sarcomere is the basic functional unit of a cardiac muscle’s cross-striated myofibril, which is defined as the boundary between two neighboring Z-lines. The I-band, A-band, H-zone and M-lines are shown. The thick filament protein is composed of myosin, cMyBP-C and titin. cMyBP-C is localized in the inner two-thirds of the A-band, i.e., the C-zone. cMyBP-C is oriented perpendicularly to the long axis of the myosin filaments. The two groups of 7–9 strips of cMyBP-C bands on either side of the H-zone give a characteristic doublet appearance within the A-band. The thin filament is composed of actin monomers, troponins (cTnT and cTnI) and α-TM, which is connected to nebulin in the I-bands.